This Stock Is Poised to Become Wall Street's Next Hot Pick
05:11 September 11, 2025 EDT
On September 10, 2025, Swedish fintech company Klarna officially listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol "KLAR." The IPO was priced at $40 per share, above the previously announced range of $35-37.
The company and certain investors collectively sold 34.3 million shares, raising a total of $1.37 billion. On its first day of trading, Klarna’s stock opened 30% higher at $52, surged to a session high of $57.2 (a 43% gain), and ultimately closed at $45.82, representing a 14.55% increase over the offering price.
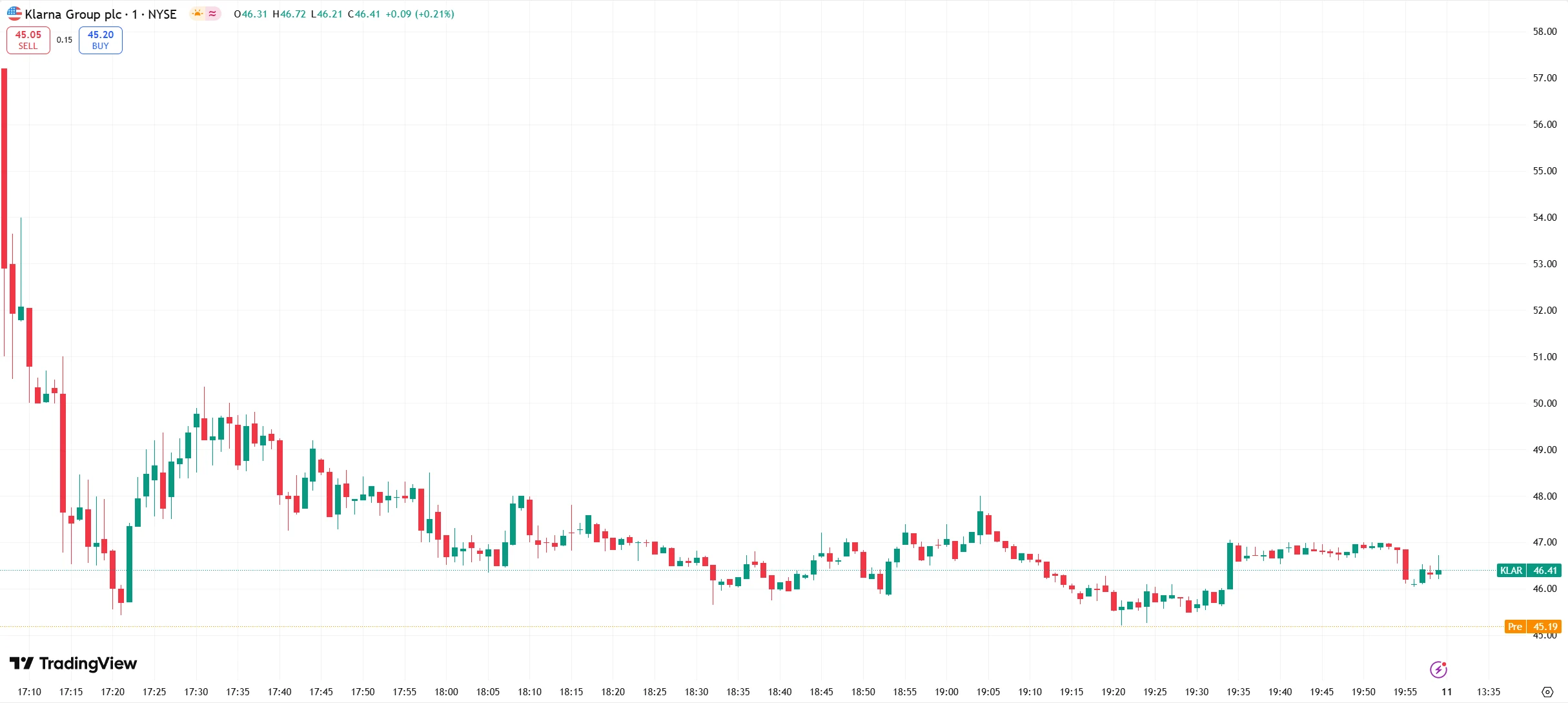
Source: TradingView
At the closing price, Klarna’s market capitalization exceeded $17 billion. This performance reflects market attention and recognition of the "Buy Now, Pay Later" (BNPL) model, while also providing investors with a potential vehicle for investment exposure to the fintech sector.
Business Fundamentals
Founded in 2005 and headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden, Klarna initially gained recognition for its "Buy Now, Pay Later" (BNPL) financing services. Under the leadership of CEO Sebastian Siemiatkowski, the company is now aggressively pursuing its transformation into a "global digital bank."
The company has expanded its business from pure BNPL services to banking products including savings, checking accounts, and credit cards. In the European Union, Klarna holds a full banking license, while in the U.S. market it has partnered with Visa to launch a debit card and become Walmart's exclusive BNPL service provider. As of June 30, 2025, Klarna operates in 26 countries worldwide, adding 26 million active users over the past 12 months. The company boasts 111 million active users and over 790,000 merchant partners, creating a powerful network effect.
Source: Klarna
Klarna's business model primarily generates revenue through merchant transaction fees and late payment charges levied on users. As global e-commerce markets develop and BNPL penetration rates increase, its transaction volumes continue to reach new highs.
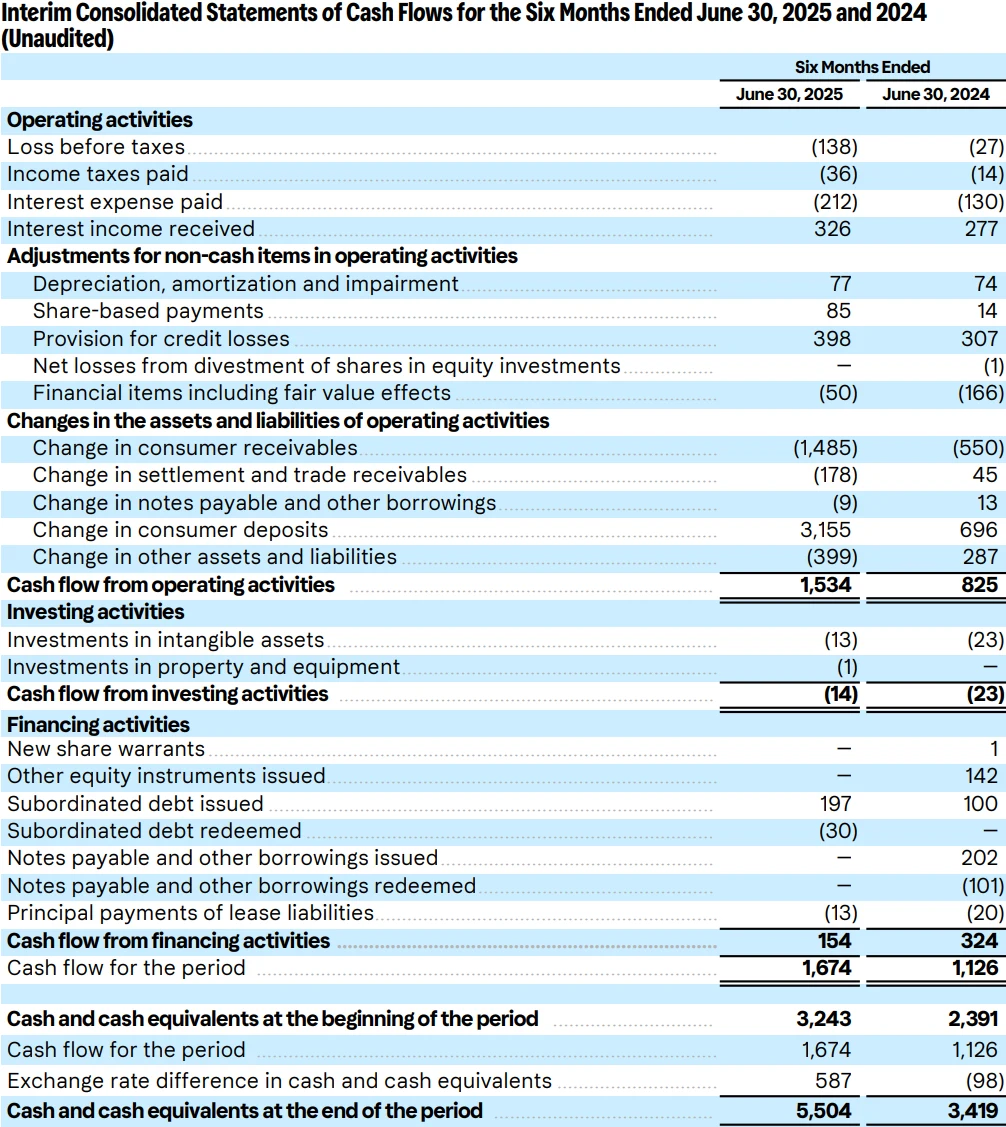
An analysis of Klarna's financial performance shows steady revenue growth trends, though profitability remains challenging. From 2022 to 2024, the company's revenue was $1.904 billion, $2.276 billion, and $2.811 billion, respectively.
In the first half of 2025, Klarna's revenue reached $1.524 billion, representing growth exceeding 15% compared to $1.325 billion during the same period the previous year. This growth primarily stems from its expansion in the U.S. market and increased transaction volumes in core European markets.
Source: Klarna
Regarding profitability, Klarna successfully returned to profitability in 2024 with net income of $21 million. This milestone marks the transition of its business model from pure scale pursuit to sustainable profitability. However, the company reported a net loss of $153 million in the first half of 2025. This volatility reflects challenges facing the BNPL industry, including credit loss provisioning and intensifying market competition.
Source: Klarna
As of June 30, 2025, Klarna held $5.5 billion in cash and cash equivalents, with customer accounts receivable of $9.95 billion and total assets of $19.189 billion.
Source: Klarna
Core Competitive Advantage
Klarna's core competitive advantages are primarily manifested in two aspects: its extensive global network effects and its powerful AI-driven risk control system.
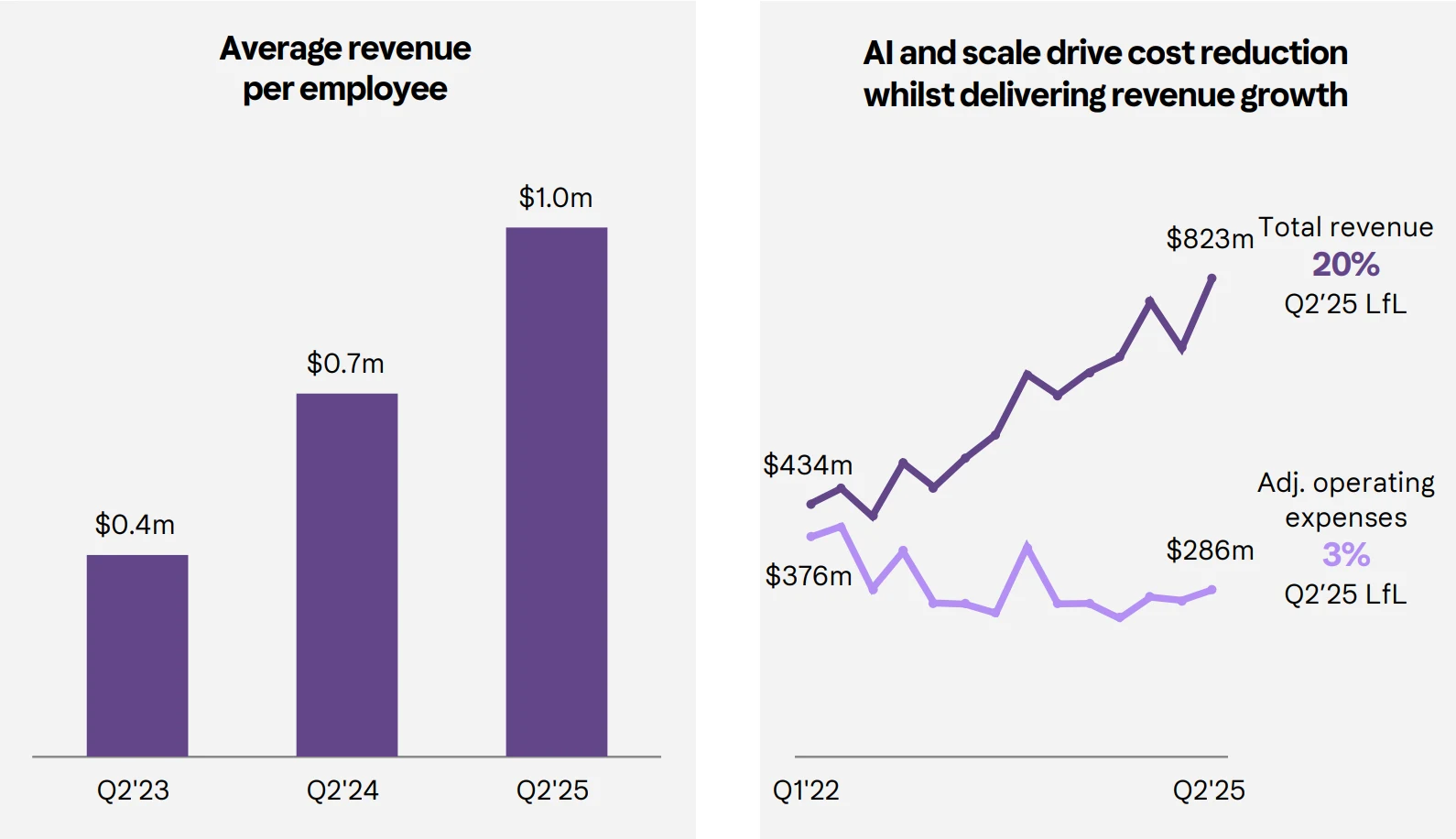
In terms of network effects, Klarna has amassed over 111 million active users and 790,000 merchant partners worldwide. This creates a self-reinforcing cycle—for consumers, an increasing number of merchants support Klarna payments; for merchants, integrating Klarna provides access to a vast user base and enhances sales conversion rates through the BNPL model.
The AI-powered risk control system represents another major competitive advantage for Klarna. Its AI-driven system can analyze massive volumes of user data in real-time, making credit decisions within milliseconds and effectively identifying and rejecting high-risk users. This enables Klarna to maintain a bad debt ratio below the average level of the U.S. credit card industry.
Klarna's AI technology is also widely applied in back-end operations such as customer service and fraud detection, significantly reducing labor costs and improving overall operational efficiency. The company projects that its revenue per employee will reach an impressive $1 million in 2025, nearly doubling from $575,000 a year earlier.
Source: Klarna
Industry Outlook
The BNPL model is reshaping the global consumer finance landscape. This payment approach allows consumers to split purchases into multiple interest-free installments, lowering psychological barriers to purchasing while effectively improving e-commerce conversion rates and average order values. Among Generation Z and millennials, BNPL has become a more popular payment method than credit cards. This trend provides Klarna with substantial growth opportunities.
The BNPL business targets an incremental consumer finance market valued at approximately $1 trillion—it does not simply replace credit cards but creates entirely new payment scenarios through features like "interest-free installments and flexible repayment," complementing credit cards and meeting the differentiated needs of the new generation of consumers.
From a regional perspective, Klarna's core markets all demonstrate strong growth prospects. Europe, as Klarna's home market, is expected to reach a BNML market size of $191.3 billion in 2025, representing a 12.4% year-on-year increase. The North American market is projected to grow by 20.4%, reaching $97.3 billion, while the Asia-Pacific region shows even stronger growth, with an estimated market size of $211.7 billion in 2025, up 14.5% year-on-year. Notably, the European market accounts for a significant share of the global BNPL landscape, and Klarna, as one of the dominant players in the region, will continue to benefit from steady local market growth.
Source: Klarna
Several key factors are driving industry growth: First, consumer demand for flexible payment options is steadily increasing, particularly among younger generations. Data shows that over 55% of Generation Z globally uses BNPL services, and this demographic's spending power and payment habits will continue to fuel market expansion. Second, the ongoing growth of e-commerce provides a broad application landscape for BNPL services. During major shopping events, BNPL can account for over 45% of payments and increase average order values by 22%. Third, offline retail penetration remains relatively low at under 15%, presenting new growth opportunities for BNPL providers.
Changes in the macroeconomic environment also bode well for Klarna. The Federal Reserve is highly likely to implement rate cuts in September 2025, which would lower financing costs for BNPL providers, reduce underwriting pressure, and stimulate consumer credit demand. A LendingTree report from April indicated that 25% of BNPL users have used the service to purchase groceries, compared to just 14% a year ago, highlighting rising consumer demand for flexible payment methods.
The gradual clarification of the regulatory environment is also conducive to the industry's long-term healthy development. Although regulatory intensity varies across regions—for example, tighter regulations in North America are increasing market concentration—the refinement of regulatory frameworks will eliminate non-compliant small players, creating a more level competitive field for leading companies like Klarna. Klarna's full banking license in the EU provides a compliance advantage that will support its continued expansion in an increasingly regulated environment.
Valuation Reasonableness
From a valuation standpoint, the pricing of Klarna’s IPO and its first-day performance reflect the market’s recognition of its value. The valuation discount relative to its competitors also provides investors with a certain margin of safety. The IPO was priced at $40 per share, above the originally proposed range of $35–$37, demonstrating institutional investors’ confidence in Klarna. Ultimately, the offering was oversubscribed by more than 20 times, further confirming strong market enthusiasm.
Compared with the industry average, Klarna’s valuation falls within a reasonable range. Diksha Gera, an analyst at Bloomberg Intelligence, estimates Klarna’s valuation to be between $12 billion and $16 billion, based on a price-to-earnings ratio of 11–14 times and a projected growth rate of approximately 12% for 2025. This aligns closely with Klarna’s market capitalization of $15.1 billion at the IPO price. The market capitalization of over $17 billion corresponding to the closing price on the first day of trading also lies within the reasonable valuation range set by analysts, with no significant valuation bubble observed.
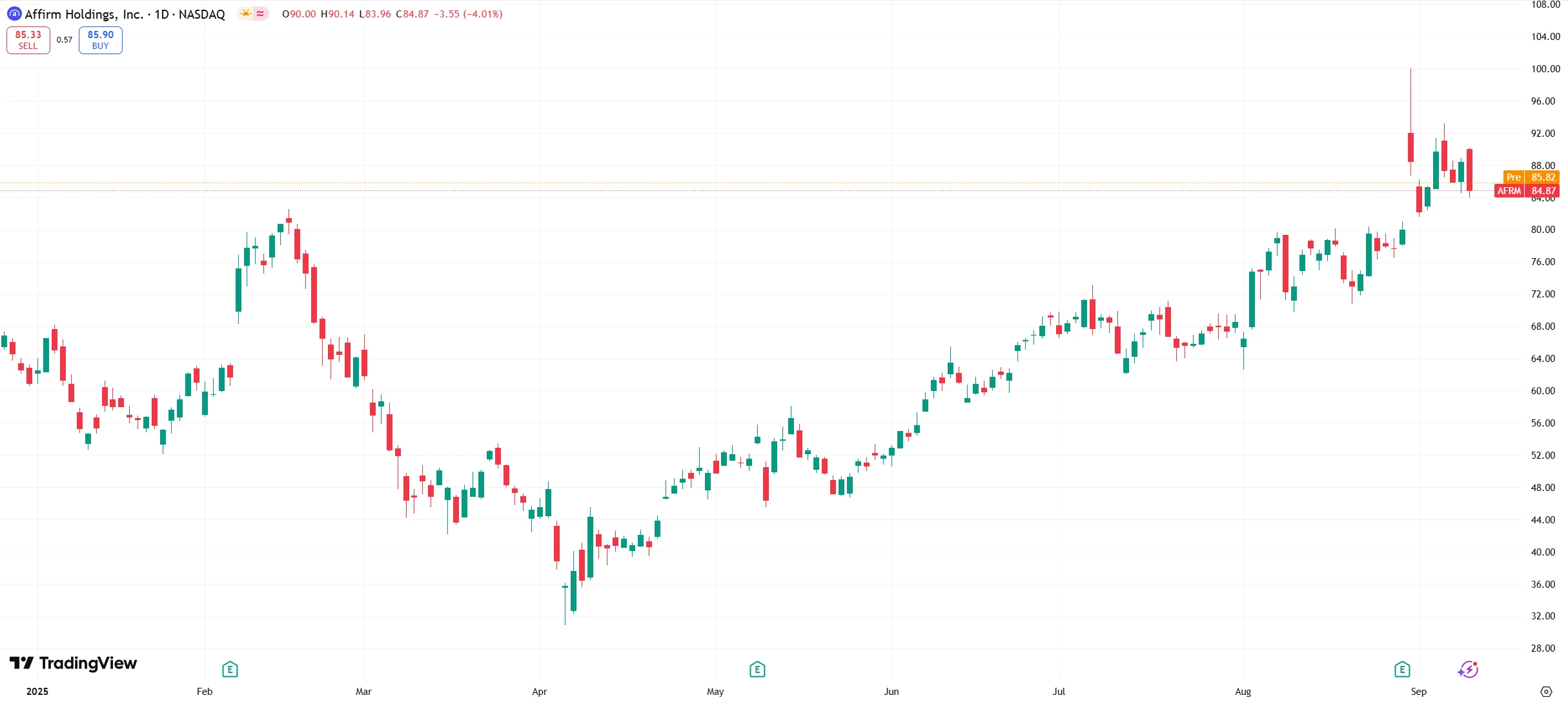
Relative to its direct competitors, Klarna trades at a certain valuation discount, offering relative appeal to investors. Prior to the IPO, analysts projected Klarna’s valuation at approximately $14.6 billion, lower than Affirm’s market capitalization of $18.2 billion at that time. This valuation gap stems primarily from the two companies’ distinct profit models: Affirm’s higher merchant fees and a larger share of interest income have enabled it to command a higher valuation multiple. Rohit Kulkarni, a senior research analyst at Roth Capital Markets, notes that Klarna should not trade at the same valuation multiple as Affirm in the short term, and this relative discount presents attractiveness for IPO investors.
Source: TradingView
From the perspective of long-term investment returns, the returns achieved by early investors also reflect Klarna’s potential for value growth. As Klarna’s largest investor, Sequoia Capital has invested a total of approximately $500 million since 2010. The IPO has generated a return of over 6 times on this investment, and based on the opening price, the value of Sequoia’s holdings has risen to $3.2 billion. Such substantial returns from long-term investments underscore Klarna’s ability to create value as an industry leader.
In terms of factors supporting its valuation, Klarna’s scale advantage and growth potential are core drivers. Despite its relatively lower merchant fees, Klarna’s gross merchandise volume (GMV) of $102.9 billion far exceeds that of its competitors. This scale advantage not only fosters network effects but also lays the groundwork for future improvements in profitability through value-added services. As Klarna transitions into a comprehensive financial services provider, its revenue structure will become more diversified, and its profitability is expected to improve further—providing support for its valuation.
Importantly, the investment thesis for Klarna is not merely based on optimism about the company’s short-term growth, but more so on a bet on the advent of a new era in consumer finance. According to the research team at RockFlow, Klarna’s long-term growth catalysts can be summarized in three key points:
1. Fundamental shifts in consumer habits: The Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) model is redefining consumers’ payment habits. Rather than competing directly with credit cards for market share, it is creating an entirely new payment scenario that meets the demands of the new generation of consumers for flexibility, transparency, and low costs.
2. Maturity of the business model: Klarna achieved profitability in 2024, demonstrating that its business model has the ability to generate organic cash flow once scaled. This transitions Klarna from a company that relies solely on financing to fuel expansion to a healthy, sustainably developing business entity.
3. Value as a "super gateway": BNPL is just the starting point for Klarna. Its vast user and merchant network gives it significant potential to become a "super gateway." In the future, Klarna can leverage its payment data to offer users additional financial services, such as personal wealth management and savings products, thereby extending its business value from the payment link to the entire consumer finance ecosystem.
An interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve will also provide additional impetus for Klarna. Lower interest rates will reduce financing costs, ease underwriting pressure for BNPL operations, and at the same time drive growth in transaction volume.
Final Thoughts
Klarna’s successful IPO is regarded as a recognition of the BNPL (Buy Now, Pay Later) model by Wall Street. Its post-listing performance will impact the IPO plans of other fintech companies, such as its European peers Revolut and Monzo.
With the shift in consumers’ payment habits and the popularization of digital banking services, Klarna represents not just a payment method, but also a transformation in the consumer finance sector. Whether it can maintain growth while achieving sustainable profitability will be a key focus for investors in the long run.
For investors, Klarna offers an opportunity to invest in the future model of consumer finance. However, they also need to closely monitor the impact of changes in the regulatory environment, evolutions in the competitive landscape, and macroeconomic fluctuations on the BNPL industry.
Disclaimer: The content of this article does not constitute a recommendation or investment advice for any financial products.

Email Subscription
Subscribe to our email service to receive the latest updates
