McDonald's MCD: Return to Value and Long-Term Growth Blueprint
16:36 September 6, 2025 EDT
Business Strategy and Outlook
McDonald's strategy emphasizes its competitive advantages through MCD: relevant marketing, core menu development, and the "Four Ds": digital, drive-thru, delivery, and growth. Recently, amidst a challenging consumer economic environment, the company has focused on leveraging scale-driven cost advantages to emphasize its value offerings. We believe this strategy is prudent.

Looking at each pillar in turn, McDonald's recent marketing initiatives have significantly boosted brand awareness. Examples include the return of Burger King, the Grimace milkshake line, and the introduction of adult Happy Meals, all of which represent recent successes. McDonald's has become more focused in its marketing efforts and has strengthened its global expansion capabilities. The company is increasingly emphasizing the strengths of its core menu, which now accounts for 65% of global system sales across its 17 billion-dollar brands, and is prioritizing menu innovation around this core strength. We are impressed by McDonald's ability to reposition its menu to meet the evolving needs of restaurantgoers worldwide. The $25 billion chicken platform now rivals the burger chain's beef platform in sales, a truly impressive achievement. Finally, McDonald's appears to be executing on its four "Ds," with its digital sales mix accounting for over 40% of system-wide sales in its key markets, driven by its base of 175 million global loyalty members, the rollout of dual drive-throughs in its restaurants worldwide, a takeout sales mix accounting for 12%-13% of system-wide sales, and a target of 50,000 stores by 2027, up from 40,000 by the end of 2022.
As competitive pressure intensifies across the industry and lower-income customers struggle amid economic headwinds, the burger chain has adjusted its strategy, emphasizing its value-oriented roots and launching a nationwide $5 meal plan with its U.S. franchisees in the second quarter of 2024. It is also seeking to drive traffic back to its stores through a reimagined value platform. These moves represent a significant turning point aimed at closing the widening value gap between the company and its industry competitors following a 40% cumulative price increase since 2019.
While the issue of satisfaction scores being below industry benchmarks has improved, if not addressed it could damage the brand and threaten McDonald's pricing power if the company fails to meet evolving customer demands.
Widespread, long-term use of GLP-1 medications may have a small but significant long-term impact on QSR traffic.
Financial strength
We assess McDonald's financial strength as solid, with the company maintaining an investment-grade credit rating and reasonable leverage relative to its competitors. Our calculations suggest a debt-to-adjusted EBITDA multiple of 2.7x by the end of 2025, below its long-term guidance range of 3-3.5x. We believe the company has robust free cash flow generation, averaging 35% of revenue by 2029, and a high EBIT-to-net interest coverage ratio (we forecast 9.3x over that period), sufficient to meet short-term debt obligations without compromising investment plans or the dividend.
While we acknowledge that private equity financing philosophies vary, we note that McDonald's leverage is significantly lower than that of its two largest fast food peers, Restaurant Brands International and Yum Brands, which have debt/EBITDA ratios of approximately 5-6x. We believe McDonald's commitment to maintaining an investment-grade credit rating is prudent, as its corporate strength often translates into more attractive franchisee borrowing rates, thereby enhancing franchisee profitability and cash flow.
Finally, the company maintains high cash flow flexibility, with clear priorities for growth capital investments, common stock dividend payments, and share repurchases. We forecast total shareholder returns exceeding $31 billion between 2025 and 2027. Cash flow remains stable due to its expanding franchise model and the appropriate alignment of future minimum rent revenue with debt repayments, and we do not anticipate credit issues for McDonald's.
Economic moat
Low barriers to entry and extremely low switching costs make the restaurant industry highly competitive, making it difficult for most operators to establish an economic moat. We believe that operators that are able to do so focus on creating pricing power through significant differentiation and highly recognizable brands, or by reducing structural operating costs. This is typically achieved through scale-driven cost advantages and systematic investments in marketing and technology, while spreading overhead costs over a larger revenue base. We believe McDonald's has a wide economic moat, as its pricing power, healthy franchise network, and successful international replication underpin its brand intangible assets. We also believe McDonald's benefits from enduring cost advantages, as its dominant global scale enables it to source food and paper at favorable prices, leverage marketing and technology investments across its global footprint, and secure lower prices from third-party delivery platforms. Our wide moat rating assumes the company can continue to generate positive economic returns over the next 20 years. Our 29% adjusted ROIC forecast for the next decade is consistent with this view, comfortably exceeding our 7% WACC estimate for the operator.
Regarding intangible assets, we believe the company's consistent ability to pass on rising food and labor costs to customers, its highly competitive restaurant margins, impressive unit sales, and its No. 1 fast-food market share by volume in all major markets (excluding China) support our wide-moat rating. First, McDonald's US and international development/franchising divisions saw average bill growth of approximately 5% annually from 2016-19, outpacing both food inflation (1.3%) and dining-out prices (2.7% increase, according to USDA data) during the same period. While the company suspended reporting this data during the initial stages of the COVID-19 pandemic due to temporary store closures, we believe the 6% annualized same-store sales growth and market share gains from 2020 to 2024 reflect the brand's competitive advantage, despite margin compression amidst unprecedented surges in input costs. We expect a full, albeit extended, recovery in profitability to pre-pandemic levels. Our view is further reinforced by the company's ability to increase its industry traffic share despite price increases exceeding 10% in 2023.
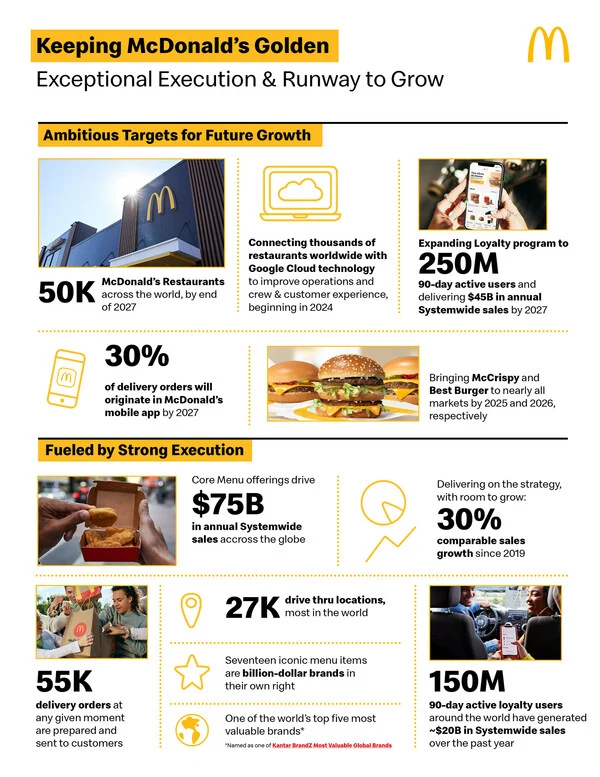
Regarding restaurant-level economics, we believe a brand's attractiveness to franchisees is determined by average unit sales, restaurant profit margins, system-wide stability, and franchise return on investment. McDonald's excels across these metrics, with average sales per franchisee in the US reaching $3.9 million in 2024, significantly outperforming its publicly traded burger peers. Given its high incremental operating margins, we estimate that higher sales will translate into higher unit operating profits than many of McDonald's direct competitors. Franchise disclosures, adjusted for comparability, confirm this view. We conservatively estimate McDonald's franchisee cash returns (annual operating income as a percentage of total cash expenditures) to be around 25%, compared to mid-single-digit to 15% returns for similar peers. This reinforces McDonald's single-unit growth strategy and enhances its appeal to franchisees. Our view is bolstered by management's guidance for accelerated near-term unit growth, with the company now targeting 50,000 net stores by 2027, an increase of approximately 10,000 units from the 40,000 units projected by the end of 2022. Encouragingly, these targets reflect a return to growth in the company's home market of the United States.
Finally, with McDonald's projected systemwide sales of $131 billion in 2024, we estimate it will capture approximately 4% of global consumer foodservice sales, roughly double the share of its closest competitor, Yum! Brands, demonstrating the company's success in replicating its philosophy internationally. With operations in 115 countries, McDonald's demonstrates brand strength that transcends geographies, tastes, and cultures. While setbacks along the way have led to shifts in business philosophy, we have been impressed by McDonald's ability to transfer winning innovations throughout the system, such as the launch of Spicy Chicken McNuggets, originally developed in China. As McDonald's migrates its international franchisees to a more homogenous technology stack, the pace of innovation will only accelerate. We believe investments in digital innovation, loyalty programs, new store formats, and the Chicken McNuggets platform indicate management is taking appropriate strategic steps to position the company for continued growth in the restaurant industry.
Regarding the company's cost advantages, we believe McDonald's scale enables it to enjoy volume discounts on food and paper purchases from food distributors, gain fixed cost leverage against general, administrative, marketing, and technology expenses, and benefit from lower fees from third-party aggregators. QSR operators prioritize cost and on-time delivery when it comes to purchasing relationships. Larger case volumes per store allow food distributors to better manage per-case delivery costs, especially in the costly last-mile delivery process, while in-house technology capabilities provide chains with an advantage in covering food expenses without adding additional services such as inventory management, marketing support, or other more profitable (for distributors) consulting services. Greater sales volume and geographic reach enable the largest national restaurant operators to benefit from purchasing leverage, with food distributors willing to accept lower profit margins in exchange for higher operating income. This impact can be significant; we've seen some restaurant holding companies estimate that centralized purchasing can save approximately 3% of annual sales (roughly 10% of food costs for most restaurants) simply due to volume-driven pricing discounts. We imagine McDonald's savings could be even greater given its substantial purchasing scale.
While marketing and technology spending can be easily overlooked, economies of scale are crucial when building an international brand. With a 4% marketing royalty and projected systemwide sales of $131 billion in 2024, McDonald's advertising cooperatives likely have approximately $5.2 billion in marketing funds to coordinate promotions, such as the company's popular adult Happy Meals, Grimace promotions, limited-time offers, or top-of-the-funnel brand marketing through traditional print, broadcast, and digital advertising—though we note that international franchisees set their own marketing rates, so our calculated figures are only estimates. More specifically, strong brand recognition helps new locations achieve standardized average unit sales faster, shortening cash payback periods and, in turn, increasing the willingness of lenders and franchisees to work with the burger chain. Consequently, McDonald's ranks fifth among all US restaurant chains in terms of existing loan relationships and seventh in terms of loan intent in 2024, respectively—a significant advantage in an environment where banks are increasingly discerning about their financing decisions.
On the technology front, we see significant progress. McDonald's has launched scheduling software (RGM Boss) in China, boosting restaurant profitability by 30 basis points; invested in inventory management and convenient RFID tracking software; standardized functions and best practices across finance and HR data through its Global Business Services (GBS) initiative; and invested heavily in its "My McDonald's" loyalty program. With $131 billion in systemwide sales and over 43,000 restaurants worldwide by the end of 2024, McDonald's is uniquely positioned to reap the rewards of technology investments, even with modest improvements in comparable sales or restaurant margins—an advantage that smaller peers cannot replicate. As McDonald's loyalty program customer base continues to grow (penetration is expected to increase from 8% in 2023 to 14% in 2027) and McDonald's continues to enhance its unparalleled insights into customer ordering behavior, we expect the company's ability to leverage digital learning to accelerate, thereby gaining a structural advantage in pricing decisions, personalization, and even restaurant location selection. In fact, McDonald's technological prowess not only reflects its cost advantage but also serves as the cornerstone of its brand's intangible assets. Effective technology implementation will undoubtedly boost the company's revenue and profits in ways that are difficult for its competitors to replicate.
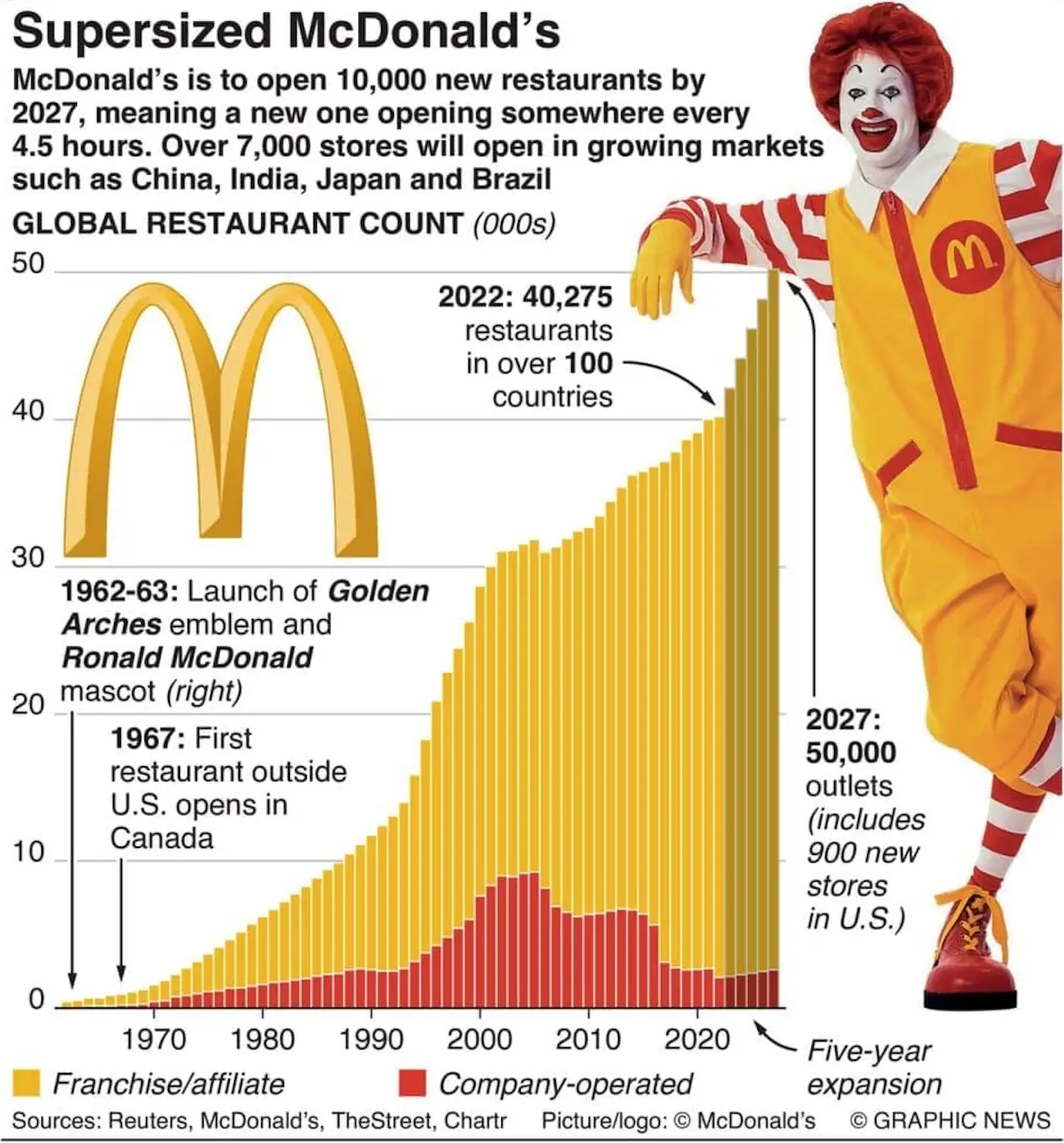
We believe an underappreciated manifestation of McDonald's cost advantage lies in its ability and willingness to reinforce the health of its franchise system, beyond pure unit economics. In the context of continued soaring food costs, McDonald's commitment to selectively and temporarily boosting profitability for its European franchisees (expected to be $100 million to $150 million in 2023) demonstrates a competitive advantage that only the world's largest restaurant operating company could undertake. This support helps avoid costly store closures and demonstrates McDonald's commitment to maintaining franchisee profitability. As consumers increasingly seek value, McDonald's also allows franchisees to invest in long-term customer relationships, lower inflation expectations, and increase industry traffic share. Rent relief during the 2020 COVID-19 outbreak played a similar role, helping to catalyze a series of impressive subsequent performance results that solidified McDonald's dominance in the global restaurant industry.
Finally, while restaurants and third-party meal aggregators are notoriously opaque regarding contractual structures, we believe the commissions McDonald's pays to aggregators like DoorDash and Uber Eats (low double digits) are lower than those of smaller peers and well below the overall commission rate of 30%. As a relatively early entrant into the space, McDonald's likely enjoyed lower commissions by partnering with Uber Eats in 2017; its subsequent agreement with DoorDash in 2019 coincided with the peak of price competition. Both agreements were renegotiated in 2021 as global deals. Management commentary from food delivery companies supports this view, as fast-food companies are widely viewed as operating at a loss—necessary to attract new consumers but with significantly lower margins than independent restaurants and small brands that rely on aggregators to generate demand.
Fair value and profit drivers
After updating our second-quarter performance model, we have raised our fair value estimate for McDonald's from $312 to $317 per share. This increase is primarily due to the impact of the time value of money on our model. In the earnings report, management maintained its full-year outlook for net restaurant growth, projecting it to contribute slightly over 2% to systemwide sales growth and an operating margin of around 40%, consistent with our pre-earnings call forecast. Therefore, we are essentially maintaining our previous forecast.
Overall, the company appears to be taking the right remedial actions, leveraging its scale-driven cost advantage—one of the two pillars of our Broad Economic Moat rating—and has begun to reverse consumers' declining value perceptions through the introduction of its "McValue menu," with offers like "buy one, get one for $1" and the company's much-touted $5 combo meal. Importantly, the company also maintained its goal of 50,000 stores by 2027 and plans to increase capital expenditures by $300 million to $500 million annually in the near term to strengthen its shared services program (Global Business Services, or GBS), both of which should create long-term shareholder value. It's certainly good to see McDonald's continue to invest in its economic moat at a time when many of its peers are cutting back.
We remain highly optimistic about McDonald's long-term growth roadmap. The expansion of McDonald's 175 million loyal customers worldwide is complemented by initiatives to increase store throughput, and its ambitious store expansion target of 50,000 stores by 2027 appears within reach. McDonald's investments in standardized global support services and the deployment of technological innovations across all markets, including developing and franchised markets, should strengthen its "four walls" economic model, solidify its growth narrative, and add to its already impressive growth story.
We are impressed by McDonald's ability to maintain strong same-store sales growth despite navigating a global pandemic, digital transformation, and the divestiture of its primarily company-owned Russian market. While 2024 marks a more challenging year for the burger giant (a year in which US same-store sales are essentially flat), the company still achieved average annual same-store sales growth of nearly 6% in its home market from 2020 to 2024 despite the extremely challenging environment, offsetting a significant portion of historically high inflationary pressures without outperforming its core customers. As the industry environment becomes increasingly promotional, we do not expect McDonald's restaurant profit margins to fully recover to pre-pandemic levels until the second half of 2025, but combined with our estimate of improved same-store sales performance, we expect significant improvement in 2026 and 2027.
We believe McDonald's has ample investment capacity throughout the cycle, while smaller, less-capitalized peers have reduced investment and struggled to absorb rising input costs. This presents an opportunity for McDonald's to continue gaining market share over the medium term, particularly in markets with high independent restaurant penetration. Driven by its burger giant's burger program, surging digital sales, and store expansion, we expect the burger giant to continue gaining market share overseas. We forecast average annual sales growth of 6.2% and 8.2% in its international operating markets and international development and licensing markets, respectively, through 2029.
Our operating margin assumption is primarily driven by operating leverage and a favorable mix shift, with McDonald's selling, general and administrative expenses declining from a peak of 12.6% of sales in 2020 to 8.9% of sales in 2034, as depreciation normalizes after significant investments in restaurant renovations.
Price and Fair Value
Based on our quantitative approach, we believe McDonald's deserves a Morningstar Low Uncertainty Rating. Due to its highly franchiseable structure and recession-resistant value proposition, the company's cash flow appears relatively insensitive to macroeconomic health.
We believe McDonald's is one of the industry's most advantaged operators, but we note that consumer pressures are likely to drive a slight shift in its product mix toward relatively affordable, stay-at-home foods (groceries), which could weaken its near-term sales momentum and pricing power. Industry traffic remains subdued, and increased discounting and promotions mean limited same-store sales growth through 2025, putting margins under pressure. Franchisees face even more pressing concerns, as their margins are likely to remain flat or decline year-over-year, while also grappling with modest increases in commodity, labor, and real estate costs.
Considering environmental, social, and governance factors, we believe human capital is the greatest risk facing McDonald's, a view shared by most restaurant operators we cover. More specifically, operators will be forced to accept California's higher restaurant minimum wage and revised National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) joint employer rules, which will lead to increased labor costs and regulatory responsibilities. California's AB 1228 mandates an industry-wide minimum wage of $20 per hour starting April 1, 2024, forcing many operators to accept mid- to high-single-digit increases to maintain operational profitability. The possibility of similar legislation in other politically liberal states warrants close monitoring.
Ultimately, the company's ability to meet evolving consumer demands remains key to its success, with the strength of its brand reflected in pricing power (which accounts for a significant portion of average spend) and customer traffic. A decline in the company's brand reputation could slow unit growth, erode profitability at the restaurant level, and reduce its appeal to potential franchisees.
Capital Allocation
We assign McDonald's a Standard Morningstar Capital Allocation Rating. Our analysis assesses three key areas that we believe influence management decisions from a shareholder perspective: balance sheet strength, investment performance, and profit distribution. Our Standard Rating is based on a strong balance sheet, a sound investment strategy, and an appropriate assessment of shareholder profit distributions.
In terms of its balance sheet, McDonald's benefits from low systematic risk, with staggered debt maturities and an extremely low net debt-to-enterprise value ratio. This offsets its relatively high leverage (historically targeting 3-3.5x EBITDA), even for a company-owned restaurant operation of its scale. Nevertheless, its highly franchised operating model reduces cash flow uncertainty, and the company's real estate portfolio provides valuable tangible assets, an unusual feature for a heavily franchised restaurant operator that can alleviate the concerns of many creditors.
We believe the investment decision is sound, and returns on invested capital will continue to grow over our defined forecast period as the company benefits from operating leverage and a modest shift toward more heavily franchised international markets. We also believe the company's decision to significantly refranchise its US stores between 2015 and 2018 was prudent, increasing the percentage of franchised stores from 81% to 95% and saving $250 million in general and administrative costs, although this arguably came at the expense of US store growth. To date, the company has struck a good balance between operating a highly franchised, decentralized system and continuously investing in store performance and unit economics, which represents a key investment risk for franchisees in this sector. Recent technology investments are encouraging, and diverse ordering methods, personalization, and targeted promotions are likely to become cornerstones of the future of the restaurant industry. McDonald's' ability to create a compelling end-to-end customer experience is crucial, as the increasing number of touchpoints within the system will provide McDonald's with access to previously unavailable data on ordering patterns, customer trends, and menu preferences across demographics. Whether McDonald's can successfully leverage this data remains to be seen. While we remain confident in the management team's ability to execute on the initiatives already implemented before the pandemic, our Neutral rating reflects our wait-and-see approach to McDonald's willingness to make bold, accretive investment decisions going forward. McDonald's Global Business Services (GBS) initiative, announced at its December 2023 Investor Day, appears to be a positive move, centralizing data and more standardized functions (finance, legal, and HR) across markets.
Finally, we will evaluate shareholder dividends as appropriate. We expect the company's dividend to grow at a low double-digit rate over the next three years, with a payout ratio of approximately 55%-60%, and we anticipate shareholder returns of slightly over $31 billion over that period. Share repurchases, as long as the company's stock price is trading below our fair value estimate, are an attractive use of capital. We believe the company has done an excellent job of avoiding imprudent spending and value-dilutive investments, maintaining a strong return on invested capital, and focusing on store expansion in more attractive international operating markets and developed/franchised international markets. McDonald's position as a landlord and its willingness to purchase the land beneath its stores creates a degree of capital discipline not often seen in other companies in the industry.
Disclaimer: The content of this article does not constitute a recommendation or investment advice for any financial products.

Email Subscription
Subscribe to our email service to receive the latest updates
