Key Reasons to Buy and Hold NVIDIA Ahead of Its August 27 Report
04:40 August 19, 2025 EDT
Key Points:
Nvidia is set to release its FY2026 Q2 earnings on August 27, with analysts projecting revenue of $45.5 billion and EPS of $1.00.
In FY2026 Q1, despite H20 export restrictions, the China market still contributed $4.6 billion in sales, and with the market reopening, further revenue growth is expected.
For investors, given Nvidia’s attractive valuation and long-term growth catalysts, positioning ahead of the earnings release remains a reasonable investment strategy.
As Nvidia prepares to report its FY2026 Q2 earnings on August 27, investors are focusing on the sustained growth of its data center business and valuation dynamics. Against the backdrop of accelerating AI infrastructure development, Nvidia’s technological and ecosystem advantages are reinforcing long-term earnings visibility—an important reason for investors to consider building positions before the earnings release and holding for the long term.
Earnings Report Key Focus
The market’s primary focus remains on the sustained growth of Nvidia’s data center business.
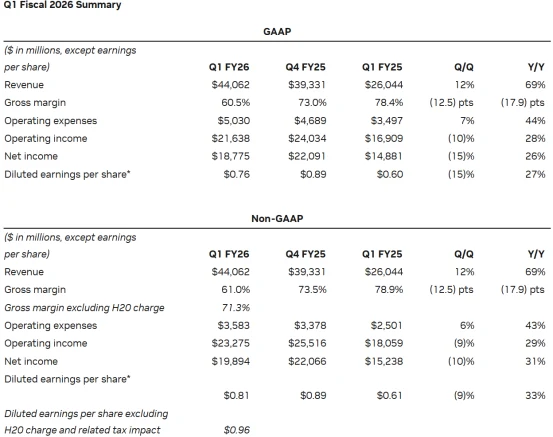
Nvidia’s FY2026 Q2 revenue guidance is $44.1 billion to $45.9 billion, with a midpoint of $45.0 billion and a 2% range of variability. This builds on Q1 revenue of $44.1 billion, including $39.1 billion from the data center segment (up 73% year-over-year). Analyst consensus projects Q2 revenue of $45.5 billion, with Cantor Fitzgerald’s C.J. Muse forecasting as high as $48.0 billion, while Morgan Stanley offers a more conservative estimate of $43.5 billion. These projections reflect optimism about increased Blackwell GPU shipments and sustained AI training demand.
Source: Nvidia
On the profitability side, Nvidia expects adjusted non-GAAP gross margins of 71.5% to 72.5%, with a midpoint of 72.0%. Analysts’ average estimate is 71.7%, indicating stable margin expectations. In FY2026 Q1, GAAP and non-GAAP gross margins were 60.5% and 61.0%, respectively, affected by specific factors. U.S. export restrictions on H20 products to China reduced demand, resulting in $4.5 billion in costs from inventory build-up and procurement commitments. Excluding these costs, Q1 non-GAAP gross margin would have been 71.3%.

Source: Nvidia
Non-GAAP EPS for Q1 was $0.81, excluding the $4.5 billion H20-related export restriction costs, supporting the possibility of Q2 EPS reaching $1.00. FactSet data show analysts generally expect EPS of $1.00, with a range from $0.86 (TipRanks) to $1.06 (C.J. Muse), suggesting upside potential if Blackwell chip adoption accelerates.
Drivers of Earnings Growth
Morgan Stanley data indicate that in 2025 alone, the four largest hyperscale companies are expected to invest up to $300 billion in AI infrastructure. Omdia forecasts that by 2029, the cloud computing and data center accelerator market will reach $151 billion. As data center business continues to expand, Nvidia, as the industry leader, is well-positioned to benefit.
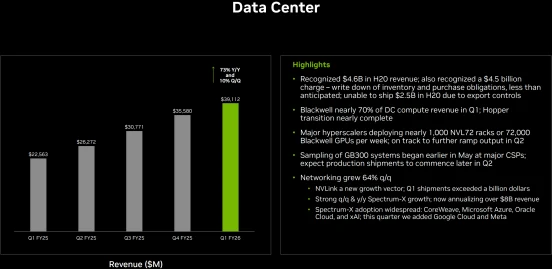
In Q1, compute revenue within the data center segment reached $34.155 billion, up 76% year-over-year, while networking revenue totaled $4.957 billion, up 56% year-over-year. These figures reflect that generative AI has moved from training to inference, driving broad demand for inference-related GPUs and high-speed networking equipment. This trend is expected to continue into Q2, further boosting data center revenue.
Source: Nvidia
Although AMD and Intel are competing for certain inference and specific training workloads with chips like MI300X and Gaudi3, structural factors—such as the CUDA ecosystem barrier, NVLink interconnect advantages, and priority access to high-bandwidth memory—limit their ability to challenge Nvidia’s 70%–80% training market share in the near term.
Potential U.S. government and Intel equity collaborations may increase Intel’s manufacturing capacity, but they do not alter the dominance of the CUDA development environment or Nvidia’s platform leadership. Similarly, while TSMC’s CoWoS advanced packaging capacity is expanding, Nvidia has already secured key resources. Capacity increases from SK Hynix, Micron, and Samsung are unlikely to materially change supply dynamics before 2028. These factors reinforce Nvidia’s priority position in AI chip production.
Notably, in January, U.S. President Trump announced the “StarGate” initiative, pledging $500 billion to build American AI infrastructure, with multiple Middle Eastern countries committing similarly large sums. Leveraging its leading chips and data center capabilities, Nvidia is involved in nearly all sovereign AI infrastructure projects, serving as a core supplier for national-level AI systems. Citi expects this market to contribute billions of dollars in revenue to Nvidia between 2025 and 2026, supporting sustained future growth.
Importantly, for most of 2025, China represented a major challenge for Nvidia. Following an agreement with the U.S. government, the company can re-enter the Chinese market, although 15% of sales must be repatriated to Washington. Nvidia’s pricing power mitigates the impact on margins. Despite H20 export restrictions in Q1 FY2026, China still contributed $4.6 billion in revenue, and as the market reopens, further revenue growth is expected.
Investment Attributes
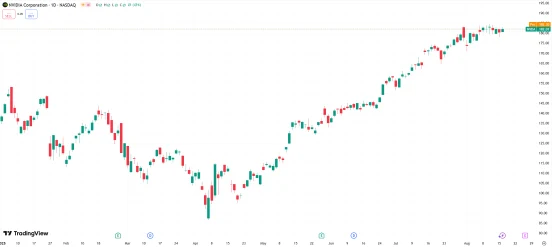
As of publication, Nvidia’s stock was trading at $182.01, representing a 35.56% gain year-to-date. Based on FY2026 estimated EPS of $4.10, the forward P/E ratio stands at approximately 44.4x, significantly below the ten-year average of 59.2x, highlighting its relative historical valuation attractiveness. Free cash flow reached $13.2 billion in Q1, providing the company with robust financial flexibility.
Source: TradingView
Meanwhile, hyperscale companies such as Meta, Alphabet, Amazon, and Microsoft are expected to spend a combined $340 billion on AI infrastructure in 2025, signaling ample long-term growth momentum. Additionally, the StarGate initiative and Nvidia’s re-entry into the Chinese market further enhance the company’s revenue potential.
Given stock volatility, investors are advised to consider a dollar-cost averaging (DCA) approach to gradually build positions. Historical trends show that Nvidia’s stock typically experiences post-earnings buying surges, with the exception of early 2025 when competition in China and tariff uncertainties triggered a temporary decline.
Currently, among 65 analysts covering Nvidia, 48 have issued a “Buy” rating, with an average target price of $188.06, implying roughly 3.3% upside from the current $182.01 share price. Performance expectations suggest that Nvidia’s FY2026 Q2 results will continue strong growth momentum. Its multi-layered moat—spanning hardware, software, and supply chain—should maintain market leadership through 2028, even as AMD and Intel make inroads in certain niche segments.
For investors, Nvidia’s combination of attractive valuation and long-term growth catalysts supports a rationale for positioning ahead of the earnings release. A phased investment strategy can help manage short-term volatility, while close attention to the August 27 earnings call, particularly updates on Blackwell adoption and China market developments, will aid in optimizing investment decisions and capturing long-term returns.
Disclaimer: The content of this article does not constitute a recommendation or investment advice for any financial products.

Email Subscription
Subscribe to our email service to receive the latest updates
