U.S. Retail Giants Earnings Preview: Profit Divergence, Weakening Consumer Confidence
22:52 August 18, 2025 EDT
Key Points:
U.S. retailers are set to report their Q2 2025 results, while weakening consumer confidence and tariff pressures are raising concerns about the resilience of retail demand.
Analysts widely expect earnings to show a clear divergence: Walmart, with its low-price and scale advantage, may have a defensive edge, while home improvement retailers reliant on housing market strength could face headwinds.
Trends in gross margins and management forward guidance may be key for investors assessing 2025 outlook.
U.S. retail faces a “big test” this week. Home Depot, Target, Lowe’s, and Walmart are scheduled to release their Q2 2025 earnings, with weakening consumer confidence and tariff pressures fueling market doubts about retail demand resilience. Recent economic data shows consumer sentiment has declined for the first time in four months, largely due to rising price expectations driven by import tariffs.
Analysts widely expect earnings to diverge: Walmart, benefiting from low prices and scale, may maintain a defensive position, while home improvement retailers dependent on housing market health are likely to come under pressure.
Inflation Pressure and Soft Consumer Sentiment
On the eve of the Q2 2025 earnings season, the U.S. retail sector faces a complex economic environment.
The preliminary August 2025 University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index came in at 58.6, down 5.0% from July’s 61.7 and below the market expectation of 62. This marks the first decline since April, reflecting growing concerns over the economic outlook. The Current Economic Conditions sub-index fell to a three-month low of 60.9, while the Expectations sub-index dropped to 57.2.
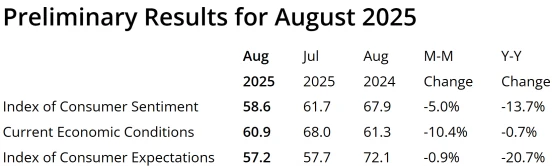
Source: University of Michigan
The primary driver of this decline is rising inflation expectations. One-year inflation expectations increased from 4.5% to 4.9%, while five- to ten-year expectations rose from 3.4% to 3.9%. Approximately 62% of consumers expect the unemployment rate to increase over the next year, and 58% plan to cut spending on autos, household goods, and dining out to offset potential inflation pressures.
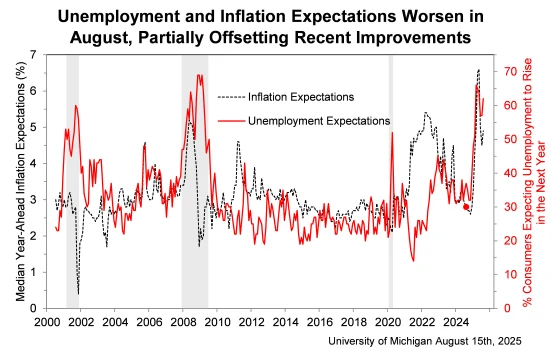
Source: University of Michigan
Tariffs have played a central role in this shift in sentiment. Since early 2025, the effective U.S. import tariff rate has climbed from 2.4% to 18.6%, the highest level since 1933. These measures target imports from China and other regions, affecting more than one-third of fresh vegetables and various consumer goods. The July 2025 Producer Price Index (PPI) rose 0.9% month-over-month, far exceeding the 0.2% forecast and marking the largest increase since June 2022. Notably, wholesale prices for fresh vegetables surged 38.9% from June to July due to tariff impacts, further fueling consumer concerns over everyday goods prices.
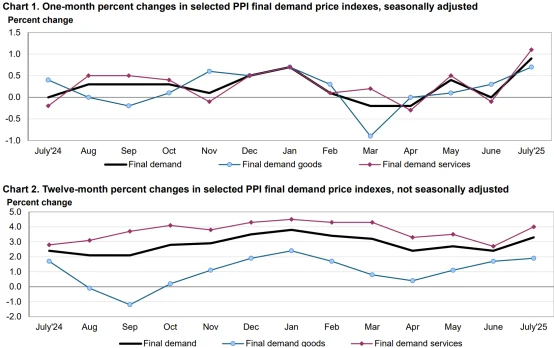
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
A July Morning Consult survey found that 51% of adults attribute rising inflation to tariffs, while 43% reported a direct impact on household budgets. For retailers, this translates into more cautious consumer behavior, especially in non-essential categories, as households prioritize value-oriented spending amid growing employment concerns. Nonfarm payrolls added only 73,000 jobs in July, below expectations, with prior months’ figures revised down, further dampening spending confidence.
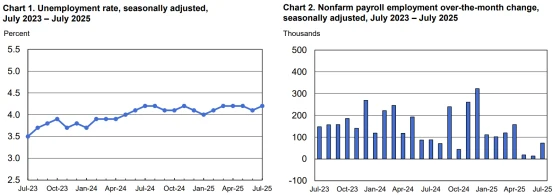
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
Tariff Pass-Through Effect
Tariffs represent a major headwind for the U.S. retail sector, particularly for companies reliant on imported inventory. The 30% tariffs on Chinese goods and 10% retaliatory tariffs on U.S. exports have driven up procurement costs.
Take Walmart as an example: roughly one-third of the products it sells in the U.S. are imported, with about 60% sourced from China. Tariff costs are passed along the supply chain, resulting in landed costs for some products rising by more than 100%. Despite Walmart’s efforts to diversify its supply chain—such as increasing sourcing from Southeast Asia and Mexico—the company was forced in April 2025, due to inventory pressures, to absorb the new tariffs itself to maintain shelf availability. This strategy directly compresses gross margins—if tariffs were fully passed on to consumers, North American gross margins could drop from 24.7% to 9.3%, with annual profit losses potentially reaching $19 billion.
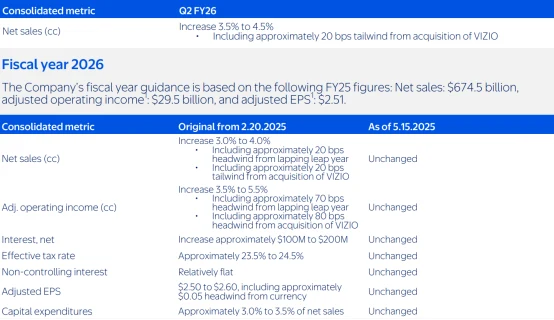
Source: Walmart
Target faces an even tougher situation. About 31% of its imported products are home goods and apparel (FY2024: home décor accounted for 15.67% of sales, apparel and accessories 15.49%). Tariffs have raised procurement costs, while weak consumer demand for non-essential categories limits the company’s ability to pass on costs through price increases. In Q1 2025, Target’s net sales fell 2.8% year-over-year to $23.8 billion, with full-year sales expected to see a low single-digit decline. To address the challenge, Target is accelerating supply chain localization and partnering with U.S.-based suppliers to develop private-label brands, but this process takes time and is unlikely to relieve profit pressures in the short term.
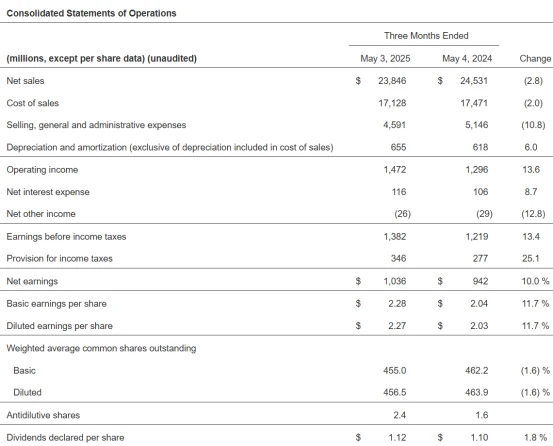
Source: Target
Home Depot and Lowe’s face additional pressures in the building materials sector, as tariffs exacerbate a slowing housing market. Analysts estimate that a permanent 5% tariff could raise retail inflation expectations in H2 2025, significantly boosting core CPI and thereby reducing consumer demand. Overall, tariffs could increase retail inflation by 1–2% in 2025, testing pricing power amid weak consumer confidence. The Yale Budget Lab estimates that tariffs could cost the average household an additional $2,400 in 2025.
Retail Performance Divergence
Retail sales data provide context for earnings reports. In July, general merchandise store sales rose 0.4% month-over-month and 2.3% year-over-year. However, home improvement sales fell 1% month-over-month and 2.6% year-over-year, reflecting category-specific weakness. Market expectations for retail companies’ performance have already incorporated these trends as well as tariffs and confidence factors.
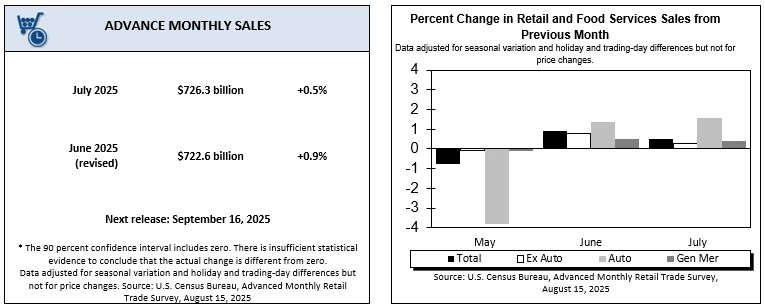
Source: U.S. Census Bureau
Consensus for Home Depot expects Q2 revenue of $45.5 billion, up 5.1% year-over-year, with EPS of $4.72, up 1.1%. The “One Home Depot” strategy emphasizes supply chain expansion and digital investments to support recovery and growth in professional customers through the SRS Distribution acquisition. However, weak demand for high-margin discretionary items and building materials tariffs limit upside potential. Housing market stagnation and hesitation on large expenditures add further headwinds.
Lowe’s is expected to report revenue of $24.0 billion, up 1.7%, with EPS of $4.24, up 25%. Sales grew slightly in May and July, while June declined 1.5%. Similar to Home Depot, Lowe’s is addressing delays in housing recovery and consumer reluctance for big-ticket purchases. Tariffs on imported tools and materials may compress gross margins, though operational efficiency provides a buffer.
Walmart outlook is relatively positive, with expected revenue of $174.0 billion, up 4%, and EPS of $0.72, up 7.46%. E-commerce sales are projected to increase 22% year-over-year, supported by 14.8% growth in Walmart+ memberships and Walmart Connect advertising revenue. In a value-oriented market, Walmart benefits from strong grocery and essential sales, despite the threat to profits from Chinese import tariffs. High-income consumer spending patterns support performance, with U.S. sales expected at $118.0 billion, up 2.9%. Institutions including Goldman Sachs expect stable growth, projecting Q4 2025 sales up 4.3% and EBIT margin at 4.4%.
Target faces greater challenges, with expected revenue of $25.0 billion, up 2.3%, but EPS of $2.05, down 20%. Q1 sales declines and confidence issues persist, with full-year guidance pointing to low single-digit sales declines and EPS of $7–$9. Investments in digital capabilities and retail fundamentals aim to drive recovery, but economic uncertainty favors discount retailers such as Walmart. Goldman Sachs maintains a Buy rating with a 12-month target of $166, based on improvements in inventory efficiency and high-margin categories such as beauty and home. Evercore ISI believes results may exceed expectations, potentially triggering a relief-driven rebound.
Investor Considerations
The S&P Retail Select Industry Index has risen only 4.9% year-to-date, lagging the broader market amid consumer headwinds. Back-to-school spending is expected to edge down slightly to $858 per household, compared with $875 in 2024, though electronics and apparel sales are driving total K–12 spending to $39.4 billion. This seasonal factor may support general merchandise retail performance in Q2.
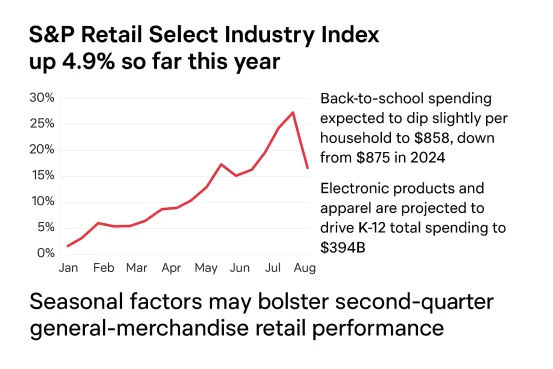
Stock performance reflects expectations: Walmart is up 12% YTD, Home Depot and Lowe’s up 2.7% and 3%, while Target has fallen 20%. Target’s forward P/E of 11 indicates undervaluation, but tariff risks warrant monitoring of guidance updates. D.A. Davidson, Oppenheimer, and Tigress Financial maintain Buy ratings on Walmart with price targets up to $120, highlighting its digital transformation efforts.
Source: TradingView
These earnings reports will shed light on consumer health, with tariffs and confidence as key variables. Better-than-expected results may signal resilience, while disappointing outcomes could highlight deepening caution. Trends in gross margins and management forward guidance may be key for investors assessing the 2025 outlook.
Disclaimer: The content of this article does not constitute a recommendation or investment advice for any financial products.

Email Subscription
Subscribe to our email service to receive the latest updates
