Paying 15% of H20 Chip Sales Revenue in China——The Impact on Nvidia’s Profit
21:33 August 11, 2025 EDT
Key points:
Nvidia has reportedly reached an agreement with the U.S. government to pay 15% of its H20 AI chip sales revenue in the Chinese market in exchange for export licenses.
The agreement applies to Nvidia’s H20 chips and AMD’s MI308 chips, with the U.S. Department of Commerce having begun issuing the relevant licenses.
This agreement may set a precedent, potentially impacting other technology companies’ business operations in China.
On August 11, 2025, the Financial Times reported a widely discussed development: Nvidia and AMD have reached a special agreement with the U.S. government, under which both companies agreed to remit 15% of their AI data center chip sales revenue destined for the Chinese market to the U.S. government as a condition for obtaining export licenses. This arrangement marks a first in the history of U.S. export controls.
According to U.S. officials, the agreement covers Nvidia’s H20 chips and AMD’s MI308 chips, and the U.S. Department of Commerce has begun issuing the related licenses.

Agreement Background
U.S. chip export controls to China began under the Biden administration, aimed at restricting advanced AI chips from entering the Chinese market. In response, Nvidia specifically developed the H20 AI GPU to comply with export regulations.
However, in mid-April 2025, the Trump administration expanded the restrictions to include a ban on H20 chip exports, forcing Nvidia to suspend sales and record a $4.5 billion inventory and purchase commitment impairment in the first quarter of fiscal 2026. During that quarter, revenue from the Chinese market amounted to $5.5 billion, representing 12.5% of total revenue, down from 14% and 15% in the previous two quarters. Without the restrictions, an additional $2.5 billion in H20 sales could have been realized.
Starting in July 2025, Nvidia informed investors that it was reapplying for H20 export licenses and expected approval soon, though the 15% revenue-sharing condition was not disclosed at that time. The agreement’s finalization signals a new approach by the U.S. government, exchanging export licenses for financial arrangements. Experts suggest this aligns with the Trump administration’s trade strategy, designed to generate fiscal revenue for the U.S. government. Nvidia responded by affirming its compliance with U.S. government rules and its commitment to continue serving customers within regulatory boundaries.
While this revenue-sharing agreement imposes additional costs, it enables Nvidia to legally resume partial supply to the Chinese market, helping to mitigate the revenue impact caused by the suspension of chip sales.
Separately, on July 31, 2025, China’s Cyberspace Administration summoned Nvidia over potential security risks related to the H20 chip. Nvidia has repeatedly denied any presence of backdoors and emphasized the importance of cybersecurity. This development may further affect Nvidia’s operational environment in the Chinese market.
Impact on Revenue
The agreement will not directly reduce Nvidia’s chip sales volume in the Chinese market in the short term, as it allows the resumption of H20 exports, thereby avoiding a complete loss of this market. According to Bernstein analysts’ estimates, Nvidia is expected to sell approximately 1.5 million H20 chips to China in 2025, generating around $23 billion in revenue. This figure represents a significant portion of Nvidia’s overall data center business revenue, considering that data center revenue reached $39.1 billion in the first quarter of fiscal 2026, a 73% year-over-year increase.
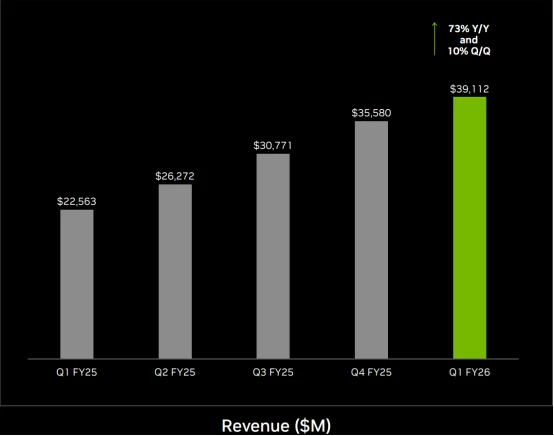
Source: Nvidia
In the first quarter of fiscal 2026, without export controls, Nvidia’s H20 chip sales to China could have reached $7.1 billion, accounting for 15.2% of total revenue. The first half of the second quarter remained affected by export restrictions, resulting in lower H20 sales and an estimated revenue loss of about $8 billion. The company’s guidance for total revenue in the second quarter is $45 billion (±2%), slightly below analysts’ average estimate of $45.7 billion, but factoring in the $8 billion loss, the guidance actually exceeds expectations.
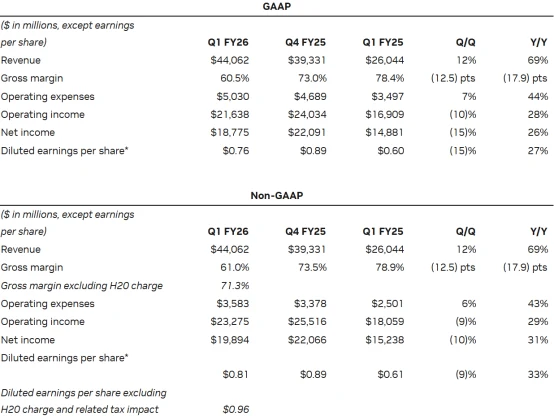
Source: Nvidia
In the third quarter, with export licenses granted, H20 sales are expected to rebound to approximately $9 billion. Under this assumption, Nvidia will pay $1.35 billion to the U.S. government, representing 15% of H20 revenue for that quarter. Relative to the company’s total revenue, this payment accounts for approximately 2% to 3%, given that first-quarter total revenue was $44.1 billion and would have been $46.6 billion without export restrictions.
In the long term, if Nvidia raises product prices due to additional costs, demand in the Chinese market may decline, indirectly impacting revenue. As China is one of the world’s largest AI markets, losing access to it would cost Nvidia approximately $50 billion in market opportunity.
However, the 15% revenue share will also directly reduce Nvidia’s profits.
Based on estimated $23 billion in China sales, the payment to the U.S. government would be around $3.45 billion. Assuming a 30% profit margin on China AI chip business, the payment would reduce profits from this segment by roughly 50%. From the company-wide perspective, the impact is limited. In the first quarter of fiscal 2026, excluding $4.5 billion in H20-related charges, adjusted gross margin was 71.3% and adjusted net profit margin was 56.1%. This indicates Nvidia can absorb a modest decline in H20 business profitability, as H20 typically accounts for about 15% of total revenue.
For the second quarter, the company expects GAAP gross margin of 71.8% and non-GAAP gross margin of 72.0%, higher than the adjusted level in the first quarter, mainly because H20 impairment charges were fully recorded in the first quarter. Analysts estimate second-quarter total revenue will grow 80% to 100% year over year, with data center business accounting for over 80%, driven primarily by global AI demand expansion. The top four clients—Microsoft, Google, Amazon, and Meta—represent nearly half of data center revenue. Even after paying the revenue share, Nvidia’s profitability remains well above the industry average.

Source: Nvidia
Conclusion
Following the disclosure of the agreement, Nvidia’s stock price did not experience significant negative impact, reflecting investor sentiment that this arrangement is preferable to a complete sales ban.
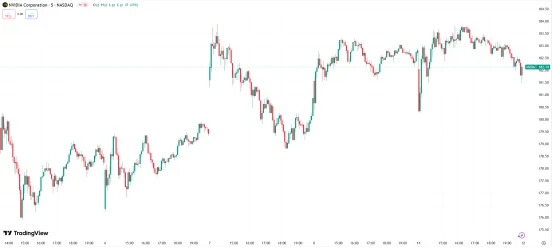
Source: TradingView
Nvidia is scheduled to release its fiscal 2026 second-quarter earnings report on August 27, 2025. Market expectations for revenue range between $45 billion and $46 billion, which aligns closely with the company’s guidance of $45 billion ±2%. In the long term, increased production of Blackwell chips is expected to drive gross margins into the mid-70% range.
CEO Jensen Huang emphasized that the Chinese market is critical to maintaining global AI leadership. This agreement may set a precedent, potentially affecting other technology companies’ business operations in China.
Disclaimer: The content of this article does not constitute a recommendation or investment advice for any financial products.

Email Subscription
Subscribe to our email service to receive the latest updates
