Apple: Winning Wall Street's $3 trillion market value with "no story"
09:15 August 9, 2025 EDT
As all the tech giants scramble to tell AI stories and restructure their valuations, Apple's performance seems particularly "boring":
The iPhone has not undergone any qualitative upgrade, Mac and iPad have declined for several consecutive quarters, and revenue for the entire year of 2024 is expected to show negative growth. The innovation story is unsustainable, and the outside world has questioned: Is this company already "old"?
However, the capital market's performance contradicted this sentiment— institutional investors increased rather than decreased, buying more and more . This raises the question: why can a company with "lack of growth potential" continue to be Wall Street's most heavily invested company?
We deconstruct this seemingly paradoxical logic from three dimensions:
Expectations are extremely low, but it is easy to exceed expectations
The market is currently extremely cautious about Apple's growth expectations. Against the backdrop of four consecutive quarters of year-on-year revenue declines, any marginal improvement could lead to a valuation reassessment. This "low pricing and low barrier to entry" approach provides investors with both offensive and defensive opportunities.
The AI cycle has just begun
Although it started later than its peers, Apple officially announced "Apple Intelligence" at WWDC 2025, marking its official entry into the "AI + terminal side" competitive path. The iPhone 16 is expected to take on the first AI hardware replacement cycle, which may mean a long-awaited reversal of volume for the hardware sector.
It's expensive, but it's stable . Apple boasts the world's strongest free cash flow and repurchase volume, exceptional liquidity, and resilient fundamentals. Compared to its competitors, which often harbour talk of an AI bubble and overvalued valuations, Apple's perceived lack of quality precisely signifies its certainty —the anchor that big money values most in volatile times.
Apple may not be sexy, but it is safe, controllable, and a "boring certainty" asset . So the question is - if the product is not new and AI started late, why is the investment so firm?
In the next part, we will delve into Apple’s financial reporting structure to see where the profit engine of this “most boring company” is hidden.
Behind the seemingly weak financial report: What happened to the profit structure?
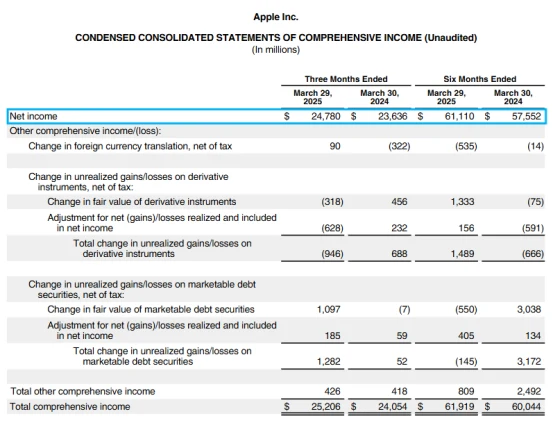
In Apple’s latest financial report - Q2 of fiscal year 2025, Apple achieved revenue of US$95.36 billion , a year-on-year increase of only +5% , and net profit of US$24.78 billion , a year-on-year increase of approximately + 4.5 % .
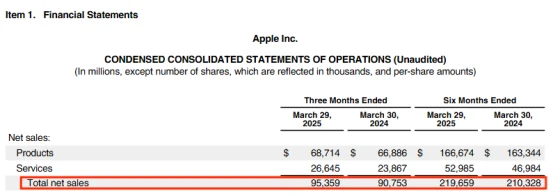
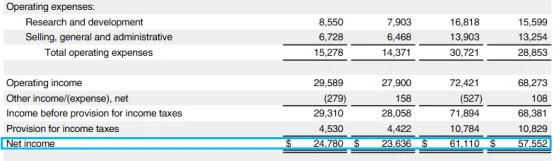
Although the financial report data seems "ordinary" on the surface, Apple's Q2 revenue only increased slightly year-on-year, and the rebound turning point expected by the market did not appear, but if we look deeper into its revenue structure, it is not difficult to find that: Apple is quietly carrying out a deep-level reconstruction of its profit logic.
1. iPhone growth is slowing, but revenue dependence is actively decreasing
This quarter, iPhone revenue reached $46.8 billion, a slight 2% year-over-year increase. On the surface, these figures are unimpressive, and the company experienced the slowest growth of all its business lines. However, the key issue isn't the "sluggish growth" but rather the declining market share : iPhone accounted for only 49% of total revenue this quarter, the first time in recent years that its share has fallen below the 50th percentile.
This means Apple is actively reducing its reliance on the iPhone and gradually shifting its focus toward services, wearables, and high-value-added ecosystems. De-centralizing the iPhone is the core logic behind this structural transformation.
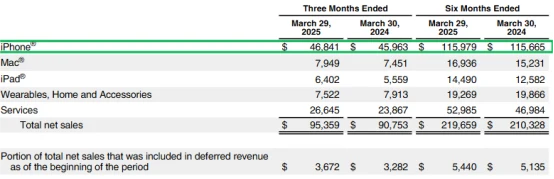
The reasons behind the sluggish iPhone revenue growth are not difficult to understand:
1. The global replacement cycle is generally extended
2. Huawei Mate 60 series makes a strong comeback in the Chinese market
3. The iPhone 15 series has limited innovation and lacks a core selling point to drive consumption.
Despite facing multiple pressures, including longer replacement cycles and intensified market competition, Apple has avoided resorting to price cuts, promotions, or frequent product iterations to boost iPhone sales. Compared to the industry's common "price war" strategy, Apple has demonstrated a more proactive "strategic restraint": proactively slowing down promotions, controlling the frequency of new product releases, and maintaining the stability of its high-end pricing structure.
This strategy isn't simply a passive contraction due to weak sales, but rather a conscious structural adjustment. Apple is gradually reducing the iPhone's dominant position in its overall business structure and shifting its growth focus to the services sector, which offers greater control, higher profit margins, and long-term expansion potential .
In essence, this is a future-oriented profit redistribution and growth model transformation, and it also indicates that Apple is redefining its profit framework in the post-smartphone era with clearer strategic logic.
2. The services business is a bright spot, becoming Apple's "high-profit engine."
Q2 service revenue reached US$26.6 billion , a year-on-year increase of +12% , setting a new record high;
the gross profit margin of the service business reached 75.7% , more than twice that of hardware products (35.9%).
Currently, service revenue accounts for more than 27.9% of total revenue , and has achieved year-on-year growth for the eighth consecutive year .
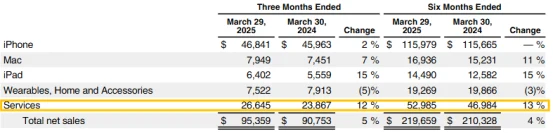
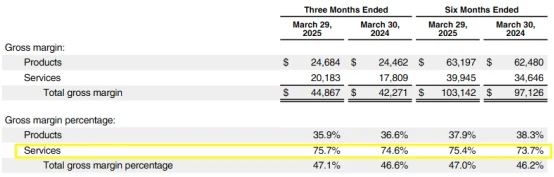
Apple's "device as platform" business model is being fulfilled: when users buy an iPhone, it is just the entry point; subsequent subscription services such as iCloud, Apple Music, Apple Store , Apple One, etc. are the real "profit gold mine."
3. Regional changes: China faces pressure, while India accelerates its rise
China's Q2 revenue was US$16 billion , a year-on-year decline of -2.3% , making it one of the few regions with negative growth.
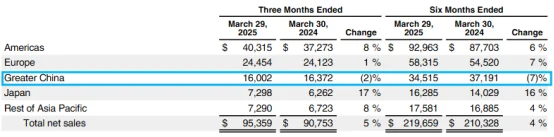
The main reasons for the decline include: the positive impact of Huawei's Mate series on the high-end market ; policies encouraging the transfer of official and educational procurement to domestic products ; and increasing pressure from geopolitics and supply chain localization .
On the other hand, the Indian market is rapidly growing . Apple has already established factories and directly-operated stores in India and is accelerating the localization of its entire supply chain.
4. Financial structure remains strong: cash, buybacks, and profit moats
Apple's operating cash flow in Q2 reached $53.89 billion (cumulative for half a year), and its free cash flow was stable.
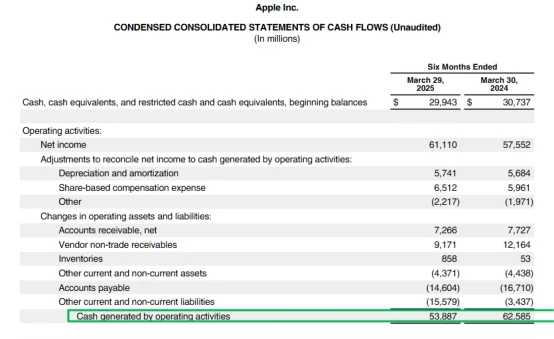
It also announced the largest stock repurchase plan in history at $110 billion , and the actual repurchase in Q2 alone reached $25 billion .
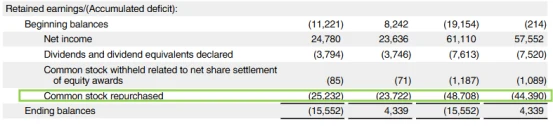
As of the end of the reporting period:
Total cash and equivalents remain at $28.16 billion
![]()
Net profit remained stable at over US$24 billion
Accounts receivable and inventory levels have declined steadily, and operational efficiency has been further optimized.
At this stage, Apple's valuation relies more on its robust profitability and strong free cash flow. The company continues to increase shareholder returns through large-scale buybacks and dividends, building a relatively solid valuation base.
From a business perspective, Apple is gradually shifting from a growth model reliant on a single hit product to one that prioritizes profit margin optimization and cash flow stability. While the iPhone remains the company's core revenue driver, its share of total revenue is declining, while the services business continues to grow, providing an increasingly significant positive boost to gross profit margins.
Overall, Apple's current revenue structure shows a stronger diversification trend, and the controllability and sustainability of its profit sources are further enhanced. Combined with the steady accumulation of free cash flow and capital return mechanism, it provides the company with stronger risk resistance in a macro-uncertain environment.
The first invisible growth line: the service empire is emerging
In recent years, Apple has gradually demonstrated a trend of transformation from a traditional high-end hardware manufacturer to a "user ecosystem platform." The core support for this transformation comes from its rapidly growing services business segment.
1) Service business structure and characteristics
Apple's service business covers App Store commissions, iCloud cloud storage, Apple Music and TV+ content subscriptions, Apple Care extended warranty services, advertising, and financial services such as Apple Pay and Apple Card.
These services are often deeply tied to devices, resulting in high stickiness and renewal rates. Due to their low marginal costs, the impact of new users on costs is limited, resulting in significantly higher overall gross profit margins than hardware businesses and relatively stable revenue growth.
2) Service and hardware collaboration model
Apple's "hardware-driven services" model has formed a closed loop. After purchasing a device, users often access Apple's services, such as cloud storage, content subscriptions, and payment systems, thus forming a stable, long-term revenue stream. This type of service revenue is highly predictable, stable, and has the characteristics of compounding interest.
3) Financial and advertising businesses have expansion potential
Apple continues to expand in the financial services sector, including launching products such as Apple Card, savings accounts, and installment payments, and establishing partnerships with financial institutions such as Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, and Mastercard to increase its market share in payments and consumer finance.
In addition, the advertising business is growing gradually based on App Store search ads, which have high gross profit and data protection characteristics, and is expected to have room for growth in the future.
Overall, the services business has become one of the most resilient and profitable segments of Apple's revenue structure, providing a growing foundation for its overall valuation. This transformation is also enabling Apple to gradually transition from a one-time sales model to a sustainable revenue model driven by user lifetime value.
The second invisible logic: the long-term foreshadowing of Apple Silicon and the AI device matrix
In recent years, Apple has launched a series of low-level AI deployments, the key foundation of which comes from its in-house chip development (Apple Silicon) strategy, and has gradually built a local AI computing capability system covering multiple terminals:
1) Apple Silicon: Infrastructure for local AI computing power
The M4 chip boasts 38 TOPS of AI computing power, a 60% increase over the M2 chip. It supports running lightweight, large language models locally and offers offline AI processing capabilities without relying on the cloud.
2) iPhone 16: A key node in the transition to AI terminals
The iPhone 16 Pro is equipped with the iOS 18 operating system, which introduces AI functions such as image and text generation, voice recognition, and text summarization. It has the ability to run locally and has been optimized in terms of performance, energy efficiency, and privacy control.
3) Vision Pro: Part of the Edge AI Ecosystem
Vision Pro is equipped with Apple Silicon chip, supports spatial audio, eye tracking, gesture recognition and other features, and forms an edge-to-edge AI and multi-terminal collaborative ecosystem with other Apple devices.
4) AI-related acquisitions: Focusing on efficiency and experience optimization
Apple has made a number of mergers and acquisitions in the fields of model compression, low-power inference, image rendering, music generation, etc., and has integrated its layout around improving AI efficiency and optimizing user experience.
Overall, Apple's AI deployment focuses on dimensions such as local computing power, device collaboration, data privacy, and experience consistency, forming a product ecosystem based on chips, systems, and local models.
The third growth line: Fintech + health terminals, Apple's "second curve" has quietly taken shape
Against the backdrop of widespread attention on iPhone sales, Vision Pro experience and AI progress, Apple is also continuing to advance its layout in the two fields of financial technology and digital health as potential support areas for future growth.
1. Fintech: Apple's expansion into payment and credit
Apple has built a payment and financial services system based on the iOS ecosystem, including:
Apple Pay : Covering over 80 countries worldwide, it is one of the mainstream device-based payment systems and has a high penetration rate among iOS users.
Apple Card and Apple Cash : provide credit card services and electronic transfer functions respectively;
Apple Pay Later : After its launch in 2023, Apple began to take charge of risk control, loan issuance and collection processes, further expanding its financial services capabilities.
The above-mentioned financial products and services have been launched in major markets such as the United States and have the feasibility of expanding to other emerging markets.
2. Digital Health: The Integration of Apple Watch and Health Platform
As a wearable device within the Apple ecosystem, Apple Watch already has multiple health monitoring functions, including:
ECG, blood oxygen detection, fall recognition, and physiological cycle tracking;
Mood recording, sleep tracking, mental health monitoring, etc.
This data can be centrally managed on the iPhone through the Health app, forming a personal health profile. In the future, if features such as non-invasive blood glucose monitoring are implemented, its application in areas such as chronic disease management is expected to be further expanded.
In addition, these health data have the potential to be connected to medical systems, insurance services and telemedicine platforms, forming part of medical information integration.

Although Apple continues to advance in multiple business directions, including AI, fintech, digital health, etc., there is still discussion in the external market about its "lack of growth story" or "AI lag".
There are currently two core issues surrounding Apple's AI progress:
1. There are doubts about its layout and capabilities in the field of generative AI, and it is believed that its release pace is slower than that of other technology companies.
2. Apple's market communication style is relatively restrained, and it rarely uses high-intensity marketing promotions or releases technology expectations, resulting in a lag in the outside world's understanding of its technological reserves and strategic direction.
The core of the controversy: Is AI lagging behind? Is innovation stagnating? Apple's biggest problem is its inability to tell a story.
In discussions on social media and in the tech community, negative voices regarding Apple's AI strategy are prevalent, primarily focusing on the view that "Apple is lagging behind in the field of AI." Related discussions point out:
Apple doesn’t release new models as frequently as OpenAI, Google, or Meta.
It is also not as active as Microsoft in embedding Copilot into various products;
CEO Cook has a reserved style in technology communication and market expectation management, lacking the high-profile technology narrative style set by people like Musk or Jensen Huang.
Regarding the question of "Is Apple's AI lagging behind?", there is also another interpretation of the technical path in the market:
Differences in technology deployment styles
Apple typically emphasizes three key factors when applying new technologies: user experience, security, and system integration, and is relatively cautious in its product deployment cadence.
Historical product comparison
For example, although Face ID and Apple Watch were not industry firsts, they had a stronger integration experience and user acceptance when they were launched.
Apple Intelligence's Positioning
Apple Intelligence focuses less on the capabilities of the models themselves and more on system-level integration and on-device operation. It provides AI capabilities through features like Siri responses, text-based graphics, and content summarization. These capabilities are powered by a large, optimized model, primarily deployed through implicit integration.
Privacy and Security Architecture
Its Private Cloud Compute (PCC) solution has passed audits by multiple third-party security organizations, ensuring local data processing priority and strengthening privacy protection.
Overall, Apple's AI deployment strategy differs from that of other tech companies, primarily in the depth of its product ecosystem integration rather than the frequency of releases or the degree of model openness. Whether Apple is lagging behind in AI remains a matter of differing understandings, both in terms of technology strategy and business choices.
Valuation vs. Security: Is Apple Worth $3 Trillion?
Apple's current market capitalization is approximately $3.2 trillion , and its valuation is often cited as high in investor discussions. However, judging by financial indicators such as valuation, cash flow, and risk structure, Apple demonstrates strong stability and cash flow return capabilities:
1. Valuation Level
Apple's price-to-earnings ratio isn't particularly high compared to some AI-related tech stocks. Given the generally high valuations of tech stocks, its valuation is considered to offer a balanced risk-return profile.
2. Shareholder Return Structure
Stock Buybacks : Apple is one of the largest stock buyback companies in the world. In May 2025, it announced an additional $100 billion in buybacks, and in the first half of 2025, it had repurchased $48.3 billion.
Dividend : The quarterly dividend per share increased from $0.25 to $0.26, maintaining the trend of continued growth.
Cash Reserves : As of Q2 2025, the company's cash and liquid securities totaled more than $133B.
Debt level : Long-term debt is $92.2B, the credit rating is A+ (S&P), and the overall debt ratio is at a low level.
III. Performance in a volatile market environment
Historically, Apple's beta coefficient is relatively low among leading tech companies, and its stock price volatility is lower than that of most AI stocks. During periods of rising market risk or shrinking liquidity, some institutions use it as an asset for risk management.
IV. Revenue Structure and Growth Expectations
Apple's profit distribution is mainly through repurchase and dividends, while maintaining stable cash flow growth. Its business structure includes:
AI localization deployment and terminal computing power improvement
Service business revenue continues to grow
The impact of buybacks on earnings per share
According to calculations by multiple analysis agencies, Apple is expected to maintain an annual growth rate of 8% to 12% in the next few years, with a stable growth rhythm.
Disclaimer: The content of this article does not constitute a recommendation or investment advice for any financial products.

Email Subscription
Subscribe to our email service to receive the latest updates
