NVIDIA and Intel Strike a Deal—Is AMD Facing a Real Threat?
05:34 September 19, 2025 EDT
Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) experienced significant stock volatility on September 18, 2025, with shares plunging as much as 5.8% intraday before closing at $157.92, down 0.78% for the day.
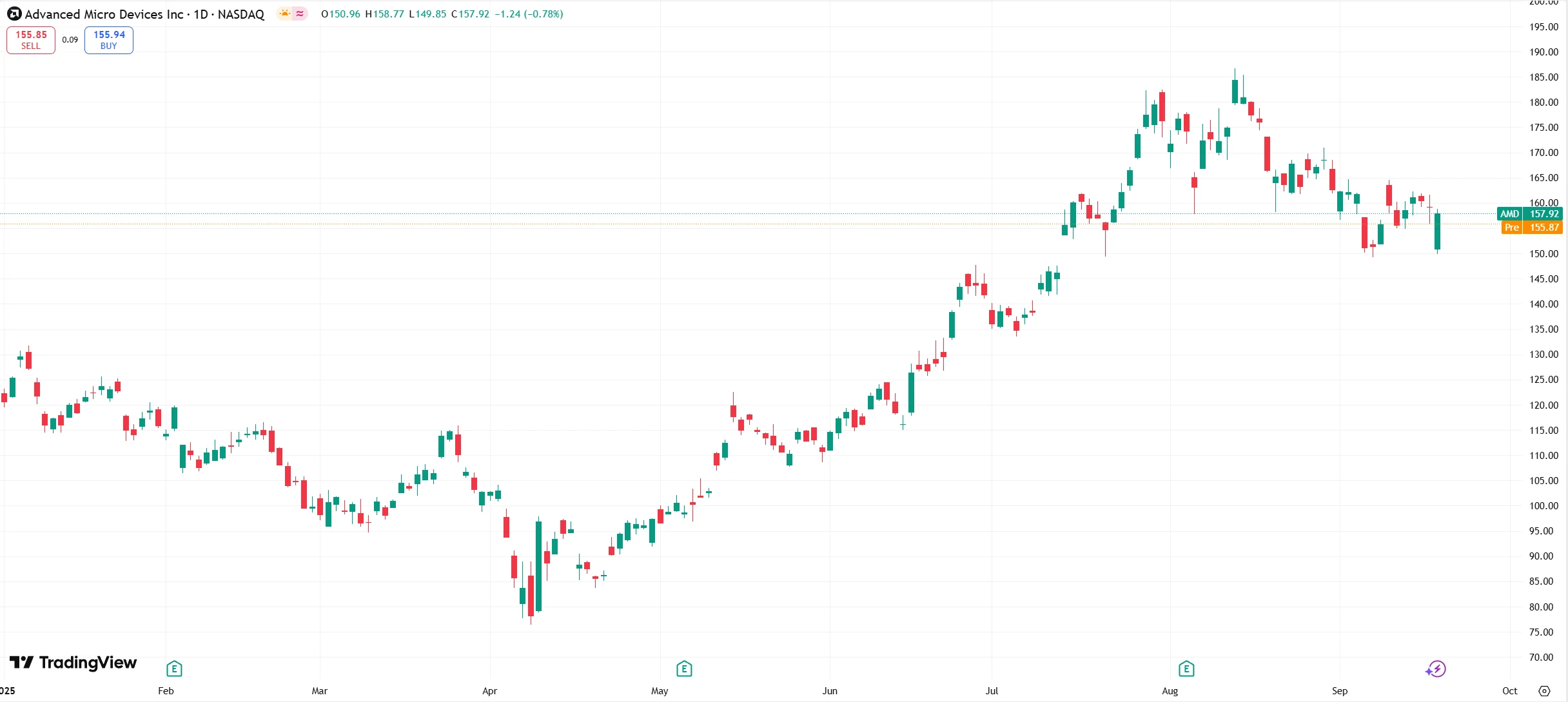
Source: TradingView
The market turbulence was primarily triggered by a surprise strategic partnership between competitors Intel and NVIDIA. NVIDIA invested $5 billion to acquire Intel shares at $23.28 per share, with the two companies set to jointly develop artificial intelligence infrastructure for data centers and personal computing products.
In recent years, Intel has struggled with declining revenue and manufacturing constraints, while NVIDIA, despite its dominant position in the AI chip sector, faces supply chain dependencies and narrowing market boundaries. This historic collaboration could signal a deep restructuring of computing architectures in the AI era.
For AMD, NVIDIA’s leadership in AI GPUs, combined with integration with Intel’s x86 CPUs, may reshape the industry landscape, posing potential pressure on AMD’s CPU+GPU business model.
Details of the Partnership
NVIDIA’s $5 billion investment in Intel secures approximately a 4% equity stake. The partnership agreement spans multiple key areas, including Intel manufacturing custom x86 CPUs for NVIDIA’s AI infrastructure platform.

Source: Intel
The two companies will also jointly develop x86 system-on-chip (SoC) solutions integrating NVIDIA’s RTX GPU dies for the consumer PC market. This collaboration leverages NVLink technology to combine NVIDIA’s AI expertise with Intel’s CPU capabilities.
In a joint statement, NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang said, “This historic partnership tightly integrates NVIDIA’s AI and accelerated computing technology stack with Intel’s CPUs and vast x86 ecosystem. It represents a convergence of two world-class platforms.”
The companies did not disclose a timeline for the first products under this collaboration. NVIDIA emphasized that its plans to develop ARM-based CPUs remain unchanged, while Intel stated its foundry business will remain neutral and may continue to provide manufacturing services to AMD—leaving room for competitive maneuvering in the industry.

Competitive Landscape
Over the past decade, the semiconductor industry has increasingly taken shape as a “three-horse race.” Intel continues to lead in the CPU market, although delays in its process technology have eroded some of its advantages. NVIDIA dominates the GPU and AI accelerator market, with its CUDA ecosystem serving as a formidable moat. AMD, meanwhile, has steadily captured market share from both competitors through its dual-focus strategy on CPUs and GPUs.
What sets AMD apart is that it is the only chipmaker competing directly with both Intel and NVIDIA. Its long-term advantage lies in the combination of CPU and GPU capabilities: Intel specializes in CPUs, NVIDIA in GPUs, while AMD integrates both through APU (CPU+GPU) solutions, delivering differentiated performance in gaming consoles, handheld devices, and other platforms.

Source: AMD
This strategy explains why Sony adopted custom AMD chips for the PS4 and PS5, and similarly why Microsoft chose AMD for the Xbox One and Xbox Series X/S. Industry observers expect that the upcoming PS6 and next-generation Xbox consoles will continue with AMD solutions, although official confirmation is still pending. Additionally, since the launch of Valve’s Steam Deck, nearly all next-generation handheld gaming PCs—such as the ASUS ROG Ally and Lenovo Legion Go—have adopted AMD chips, establishing a clear industry trend.
However, AMD’s breakthroughs remain concentrated in the consumer CPU, server CPU, and customized APU segments. In the high-end discrete GPU and AI accelerator markets, AMD still lags behind NVIDIA, particularly in data center training workloads where NVIDIA’s CUDA ecosystem maintains a strong competitive edge. At the same time, AMD’s server CPU market share has grown from less than 1% in 2017 to approximately 20–30% in 2025, posing a substantive challenge to Intel.
Amid the evolving global semiconductor landscape, the announcement of the Intel-NVIDIA collaboration has intensified concerns about AMD’s future position. In recent years, AMD has aggressively expanded across multiple markets: its server market share has risen from under 10% to roughly 30%, and its desktop CPU share has surpassed 50%, overtaking Intel in certain segments. This market pressure appears to have prompted Intel and NVIDIA to pursue their historic partnership.
NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang highlighted in a conference call that there is an underdeveloped market segment for deeply integrated CPU-GPU solutions. NVIDIA envisions leveraging NVLink technology to combine Intel CPUs with its RTX GPUs into a virtual “giant” SoC, targeting laptops and thin-and-light devices. This approach aims to save space and cost while enhancing performance and battery life, potentially creating a new category of integrated GPU PCs that directly competes with AMD’s APU strategy.
Risks and Opportunities
The Intel-NVIDIA partnership poses multiple challenges for AMD. In the data center market, Intel’s custom x86 CPUs for NVIDIA could form a powerful AI computing platform when combined with NVIDIA GPUs, directly competing with AMD’s EPYC processors.
In the PC market, Intel’s development of x86 system-on-chip (SoC) solutions integrating NVIDIA RTX GPUs could yield more competitive products, potentially constraining AMD’s growth in the consumer CPU segment.

Source: NVIDIA
Market concerns focus on the potential slowdown in AMD’s AI server adoption, particularly amid surging demand, given that NVIDIA’s CUDA ecosystem remains the industry standard. Jack Gold, an analyst at J. Gold Associates, noted: “The primary impact will be on AMD, whose chip manufacturing ecosystem differs from Intel and NVIDIA, making it unable to participate in this type of integrated collaboration.”
Despite these challenges, AMD’s fundamentals remain solid. In Q2 2025, the company reported revenue of $7.685 billion, up 31.71% year-over-year, exceeding market expectations. For Q3 2025, AMD provided an optimistic outlook, forecasting revenue of $8.4–9.0 billion (market consensus: $8.37 billion). The midpoint of this range ($8.7 billion) implies a 13.2% sequential increase. The guidance excludes any revenue from AMD Instinct MI308 shipments to China, with a projected non-GAAP gross margin of approximately 54% (market expectation: 54.1%).
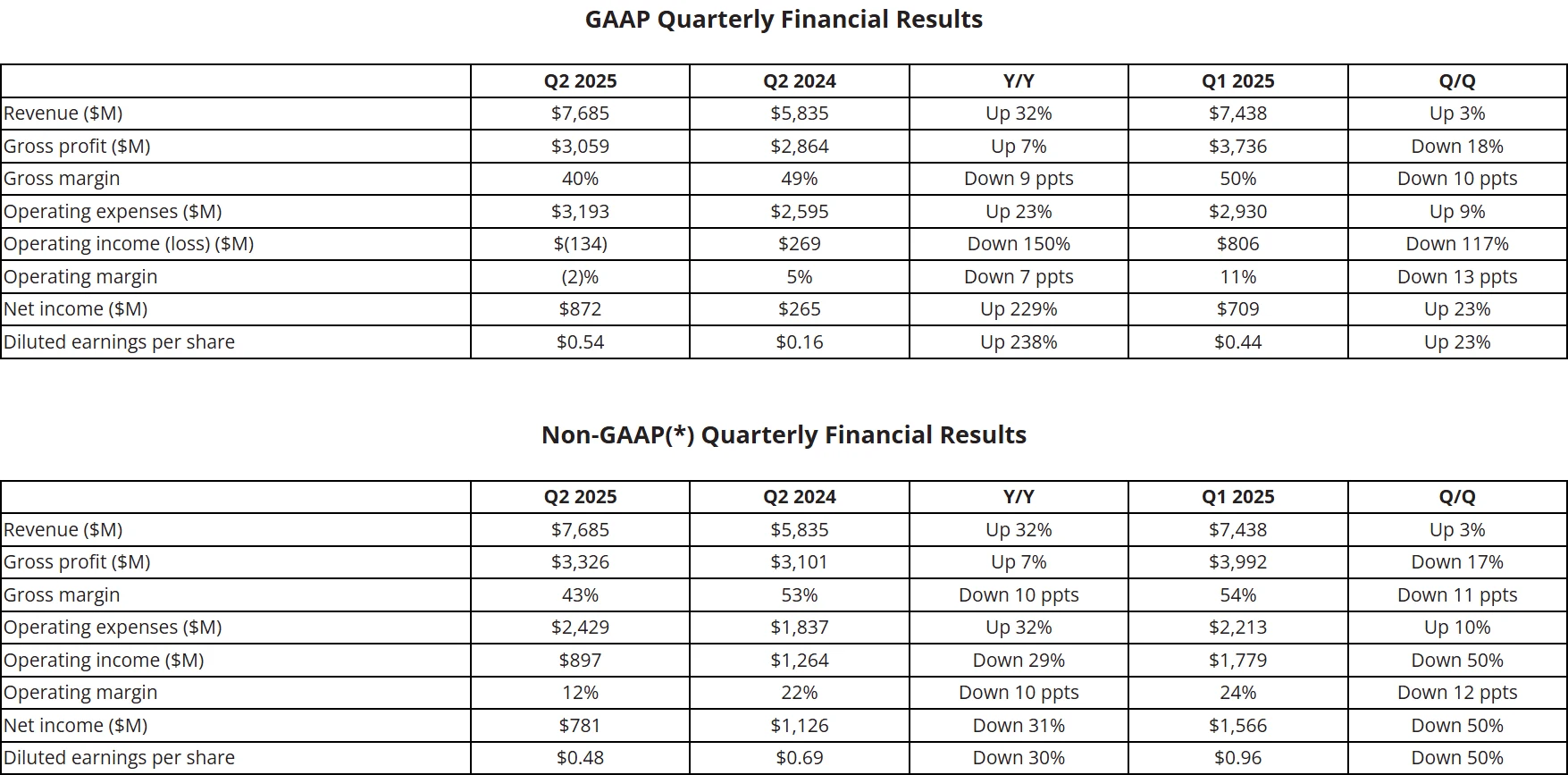
Source: AMD
On the technology front, AMD has launched its Instinct MI350 GPU series and previewed the upcoming MI400 lineup. The MI300X has already demonstrated competitive performance, featuring 192GB of HBM3 memory and 5.3TB/s bandwidth, delivering exceptional performance-per-watt efficiency for large-scale workloads.
AMD’s software ecosystem, particularly the ROCm (Radeon Open Compute) platform, has also seen significant improvements. The company has begun preparations for the ROCm 7 software stack release, promoted as a critical step toward challenging NVIDIA’s CUDA “ecosystem monopoly.”
AMD has several strategic levers to counter these challenges. The company can emphasize technological differentiation and highlight x86 architecture advantages in energy efficiency and ecosystem compatibility.
AMD has introduced the Ryzen 9 AI MAX+395 (126 TOPS of compute power) and MI300X GPU and plans to strengthen market share with the EPYC 4005 series and RDNA 4 graphics. Deepening collaboration with TSMC on 5nm and 3nm process nodes ensures manufacturing leadership. Partnerships with cloud providers such as Microsoft and Amazon for optimized AI server solutions are also viable. Additionally, AMD could collaborate with automotive manufacturers, including Tesla, to develop automotive-grade AI chips, avoiding direct competition with the Intel-NVIDIA AI stack in data centers.
From a legal perspective, AMD previously secured a $1.25 billion settlement from Intel following its 2009 antitrust lawsuit. AMD could potentially join forces with other firms to file complaints with the FTC or DOJ, alleging that the Intel-NVIDIA collaboration violates the Sherman Antitrust Act.
Market Opportunities
Despite the challenges, the AI processor market is likely large enough to accommodate multiple winners. AMD remains the second-largest player in AI processors, with little indication that it will surpass NVIDIA in the near term. By market share, NVIDIA alone accounts for roughly 90% of the global data center AI chip market, while AMD holds less than 10%. In Q1 2025, among the world’s top ten chip designers, NVIDIA retained the top spot, whereas AMD slipped to fourth due to a slight decline in its data center business and weakness in gaming and embedded products.
However, AMD is actively working to close the gap. The company projects that by 2028, the data center AI accelerator market will exceed $500 billion, with inference workloads expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 80%.
Notably, AMD’s MI350 series is scheduled to launch in Q3 2025 and has already been adopted by dozens of vendors, including Oracle, Dell, and Supermicro, which could help expand its market share. The company also unveiled its next-generation AI accelerator, the MI400, expected to leverage TSMC’s 2nm process node and deliver more than twice the AI compute performance of the MI350 series, directly targeting NVIDIA’s Rubin GPUs. Additionally, OpenAI’s decision to adopt AMD chips could provide a further boost to AMD’s position in the AI processor market.
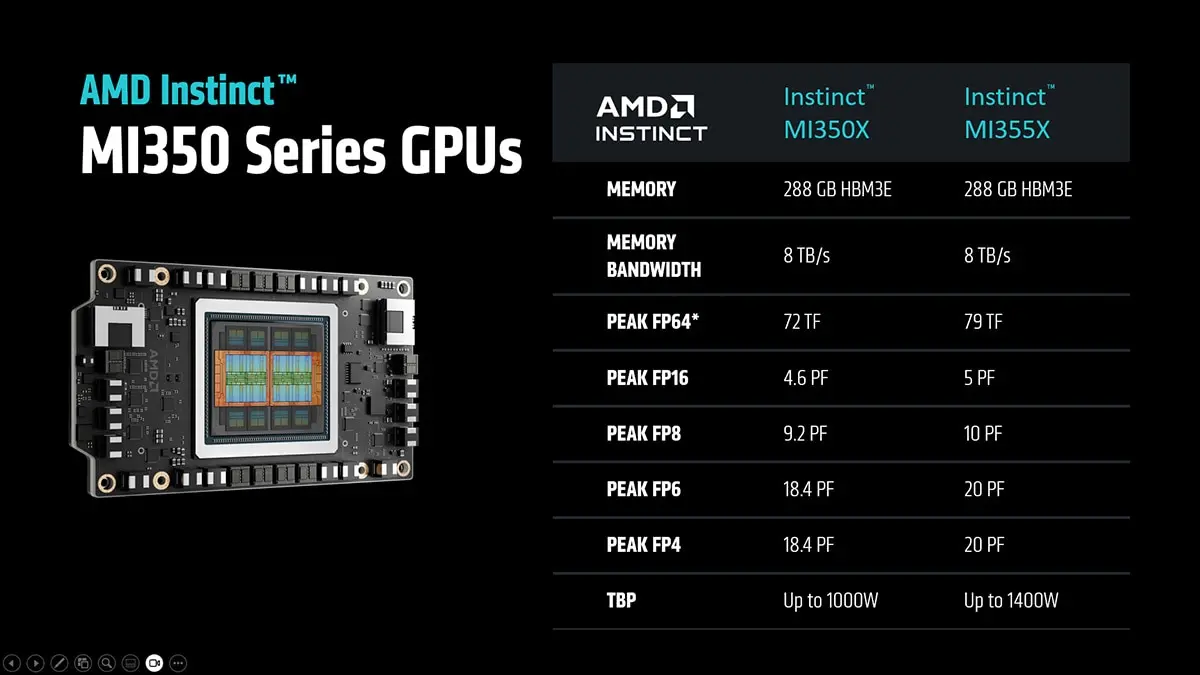
Source: AMD
Conclusion
The competitive landscape of the semiconductor industry is undergoing profound changes. While AMD faces significant challenges, history demonstrates the company’s capacity for innovation even under adverse conditions.
AMD’s share of the server CPU market has risen from roughly 10% to around 30%, and its desktop market share has surpassed 50%, overtaking Intel. These achievements underscore that there are no eternal dominators in technology markets. AMD’s strategic responses and execution capabilities will likely determine whether it can carve out new growth avenues in the face of the Intel-NVIDIA alliance.
Disclaimer: The content of this article does not constitute a recommendation or investment advice for any financial products.

Email Subscription
Subscribe to our email service to receive the latest updates
